Jenkins/Install and Plugins
Install Jenkins
Pre-requisites: Java 8
Install Jenkins on Ubuntu from repository
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add - sudo sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list' #add repo to sources.list sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install jenkins
Install Jenkins on RedHat/CentOS/Fedora
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo rpm --import http://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.key yum install -y jenkins-2.19.4-1.1 yum-config-manager --disable jenkins #disable source to prevent accidental update
Verify
cat /etc/passwd | grep jenkins #check if user has been created without shell service jenkins status #check if service is running
First run
- Password preview
sudo vi /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword - Url http://localhost:8080
- Select plugins you wish to install using web based wizard
- Once all downloaded, create your Admin user
- Once completed you will see: "Jenkins is ready! Your Jenkins setup is complete.", press Start Jenkins
Proxy if needed
If you run on restricted port system you cannot control the box firewall you may want to proxy your connection to Jenkins port :8080. You can install nGinx to do this for you
sudo apt-get install nginx
sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-enabled #then enable proxy_pass
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
}
Configure ssh keys and permissions
Required to ssh remote servers, execute bash shell scripts remotely, add slave nodes.
#generate a key pair for nologin jenkins user, while logged in as you (master) $ sudo -u jenkins ssh-keygen -f /var/lib/jenkins/.ssh/id_rsa
Jenkins master node
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname jenkins-master sudo vi /etc/passwd #make sure jenkins user have access to shell sudo mkdir -p /tank/jenkins; usermod -d /tank/jenkins jenkins #update default jenkins HOME /var/lib/jenkins directory sudo cp -r /etc/skel/. /tank/jenkins #copy .bashrc, .profile and other skeleton files sudo passwd jenkins #set a password sudo su jenkins #become ''jenkins'' user cd ~/.ssh && ssh-keygen #generate ssh key pair ssh-copy-id jenkins@localhost #add public key to Jenkins (localhost) server, these might be minions workers sudo visudo #allow jenkins sudo without password and disable requireTTY; makes easier to run builds jenkins ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL Defaults !requiretty
The !requiretty will allow Jenkins to run bash scripts in a background otherwise you receive an error:
sudo: no tty present and no askpass program specified
Build step 'Execute shell' marked build as failure
Jenkins slave (minion) worker
There is no need to install anything apart allowing the master node to ssh to it
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname jenkins-minion sudo mkdir -p /tank/jenkins sudo useradd jenkins -d /tank/jenkins #create jenkins user if does not exists, default HOME is /var/lib/jenkins sudo usermod -d /tank/jenkins jenkins #or useradd -d /var/lib/jenkins jenkins #this is default JENKINS_HOME sudo passwd jenkins #set a password, may mach the master node one but not necessary sudo visudo #allow jenkins run sudo without password prompt; makes easier to run builds jenkins ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL jenkins@master $ ssh-copy-id jenkins@slave #allow password-less ssh to slave nodes, so master can send jobs to it jenkins@slave $ ssh-copy-id ubuntu@boxes #allow password-less ssh to all other servers that Jenkins will be building/configuring
If you have any plugins on Jenkins-master node that require external programs to run you should install these tools also on slaves. As all jobs are send to slaves these external programs should be there, most common are:
- git
- java - installed automatically but you need to have Oracle Java account credentials set up in the wide configuration settings. You can also install Java yourself.
- maven
- ansible
- terraform
Jenkins Build-in CLI
Jenkins is listening on TCP port for JNLP agents. Download from http://jenkins-master:8080/cli, onto any server you wish to remotely control Jenkins
wget http://jenkins-master:8080/jnlpJars/jenkins-cli.jar
Running and connecting depends on a connection method you choose.
$ java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -s http://jenkins-master:8080 help --username jenkins --password *** $ java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -s http://jenkins-master:8080 help -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa $ java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -s http://jenkins-master:8080 list-jobs $ java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -s http://jenkins-master:8080 build 'My Awesome Jenkins Job' -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa -s -v
Running a job with multiple parameters, username position is required to be at the end; version verified here is 2.67
$ java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -s http://jenkins-master:8080 build 'Terraform' \
-p ACTION=plan \
-p LOCATION=dev11/midw/aat1 \
-p BUILD_TAG_TERRAFORM=refs/heads/master \
-p BUILD_TAG_SECRETS=refs/heads/master \
--username user1 --password password1
For passing parameters use the -p key=value flag for each parameter you want to pass.
Workaround: Under "Authorization", you want to turn on "Matrix-based security" and then for the "anonymous" user enable "Read" mode for the "Job" section.
References: isignal.github.io
Jenkins SSH
Jenkins acts as an SSH server, starting 1.446. This exposes a subset of Jenkins CLI commands (those that do not need any intelligence on the client side.) Plugins may also add additional capabilities through SSH server.
- Jenkins SSH does not require any custom jar file on the client side, making it easier to access Jenkins from a variety of sources
- Jenkins CLI client can be intelligent, performing file access and other interactive processing, whereas SSH client is dumb. Therefore, some commands can only run through Jenkins CLI and not via SSH.
REF: Jenkins SSH
Plugin manager - plugin specific version
You can download a specific version of plugin .hpi or .jpi file from Jenkins Plugins Archive page and by going to Settings > Plugins > Advanced > Upload Plugin > Browse...to .hpi/.jpi > Upload. That way you can install plugin version you want, it's opposite to upgrade/downgrade of single version only via GUI upgrade process.
Plugin: SSH Slaves plugin - adds slaves_nodes over ssh
This plugin allows you to manage slaves running on *nix machines over SSH. It adds a new type of slave launch method.
On the worker, create a workspace folder for jobs
$ mkdir ~/jenkins-minion_workspace
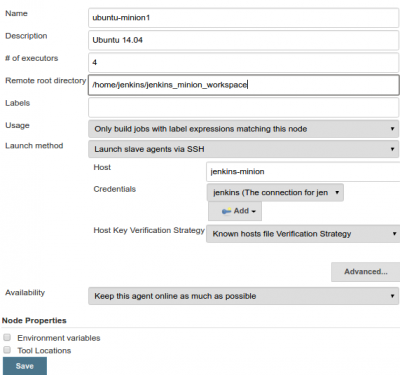
Go to Jenkins-master console and add this New Node
- Go to http://jenkins-master:8080
- Manage Jenkins > Manage Nodes > New Node with permanent agent and fill in with details
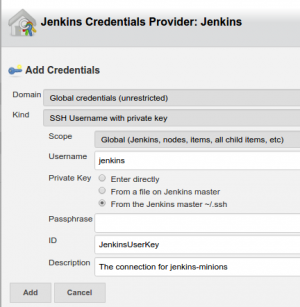
Add credentials, then select them on the main new node screen and save configuration.
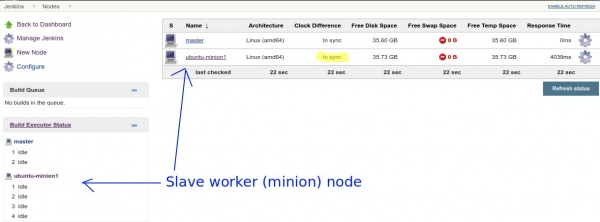
If you have Java installed on the remote worker node, all you need to do is to Launch Agent. You should see that the worker is in service and it's time in sync
Plugin: Self-Organizing Swarm Plug-in Modules
This plugin enables slaves to auto-discover nearby Jenkins master and join it automatically, thereby forming an ad-hoc cluster. This plugin consists of two pieces:
- self-contained CLI client that discovers a nearby Jenkins (via a UDP broadcast) and joins it
- A plugin that needs to be installed on Jenkins master to accept swarm clients
Download a client
wget https://repo.jenkins-ci.org/releases/org/jenkins-ci/plugins/swarm-client/3.3/swarm-client-3.3.jar
Run as anonymous user, in this case you need to enable Agent privileges on Jenkins-master node http://jenkins-master:8080/configureSecurity/ > Configure Global Security > Matrix-based security > all Agent permissions.
java -jar swarm-client-3.3.jar -name minion1 -master http://jenkins-master:8080/
Available options:
-name VAL :name of the slave -username VAL :the Jenkins username for authentication -password VAL :the Jenkins user password -passwordEnvVariable VAL :environment variable that the password is stored in
When connected you should see on slave's
jenkins@jenkins-minion-2:~$ java -jar swarm-client-3.4a.jar -master http://jenkins-master:8080/ -name minion-2 Sep 16, 2017 6:25:03 PM hudson.plugins.swarm.Client main INFO: Client.main invoked with: [-master http://jenkins-master:8080/ -name minion-2] Sep 16, 2017 6:25:03 PM hudson.plugins.swarm.Client run INFO: Discovering Jenkins master SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder". SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details. Sep 16, 2017 6:25:03 PM hudson.plugins.swarm.Client run INFO: Attempting to connect to http://jenkins-master:8080/ 8d17dd57-bef9-4be9-9633-4f00dfe45ff2 with ID 16252dd0 Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main createEngine INFO: Setting up slave: minion-2-16252dd0 Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener <init> INFO: Jenkins agent is running in headless mode. Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener status INFO: Locating server among [http://jenkins-master:8080/] Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM org.jenkinsci.remoting.engine.JnlpAgentEndpointResolver resolve INFO: Remoting server accepts the following protocols: [JNLP4-connect, CLI2-connect, JNLP-connect, Ping, CLI-connect, JNLP2-connect] Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener status INFO: Agent discovery successful Agent address: jenkins-master Agent port: 40843 Identity: 6c:9c:65:9d:4a:a3:0a:ee:1d:c4:f9:ad:a2:1b:f8:51 Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener status INFO: Handshaking Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener status INFO: Connecting to jenkins-master:40843 Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener status INFO: Trying protocol: JNLP4-connect Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener status INFO: Remote identity confirmed: 6c:9c:65:9d:4a:a3:0a:ee:1d:c4:f9:ad:a2:1b:f8:51 Sep 16, 2017 6:25:04 PM hudson.remoting.jnlp.Main$CuiListener status INFO: Connected
Plugin: Ssh plugin
This plugin allows to run shell commands on a remote machine via ssh. It provides Execute shell script on remote host using ssh option in job build section.
Install the plugin
- Install ssh plugin from Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins > click on Available tab and search for ssh
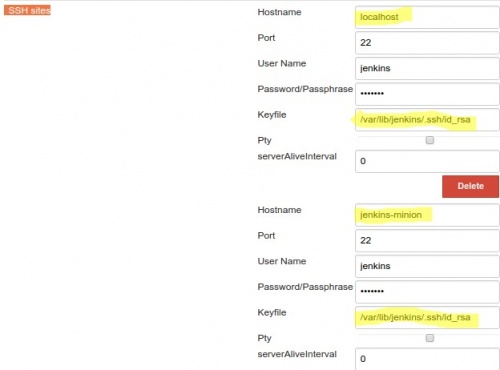
- Configure remote hosts that Jenkins can connect goto Manage Jenkins > Configure System and fill in SSH remote hosts section with similar
Add remote ssh commands project
Once ssh remote hosts are added you can create a new project and in Build section you can choose Execute shell script on remote host using ssh. You can choose remote host from drop down list that contains hosts that you configured in the previous step.
Post build actions
There is whole bunch options you can do after your build has been successful. These can be picked up in your project > Configure > Post-build Actions section from drop down menu
- Build other projects
- Email notification
Plugin: Schedule build
Use Schedule Build Plugin for this.
Plugin: Conditional BuildStep Plugin and Run Condition Plugin
Add very simple and basic condition to run this job. Write a condition in groovy script format. You can use environment variable. If the expression cannot be evaluate, false is assumed. Example : ${BUILDNUMBER} % 2 == 1 for running this job every two times or if you have a string parameter you cas use "${Name}" == "Myjob".
Working conditions:
${CONSTRUCT_APP} == true && "${ENVIRONMENT}" != "aat2"
Plugin: Performance
References
- Jmeter archive
- Tutorial I followed baeldung
- Tutorial I followed Git repo: eugenp
- Publish JMeter reports to s3
Plugin: Jenkins Job DSL
Examples
job('DSL-Tutorial-1-Test') {
scm {
git('git://github.com/quidryan/aws-sdk-test.git')
}
triggers {
scm('H/15 * * * *')
}
steps {
maven('-e clean test')
}
}
def project = 'quidryan/aws-sdk-test'
def branchApi = new URL("https://api.github.com/repos/${project}/branches")
def branches = new groovy.json.JsonSlurper().parse(branchApi.newReader())
branches.each {
def branchName = it.name
def jobName = "${project}-${branchName}".replaceAll('/','-')
job(jobName) {
scm {
git("git://github.com/${project}.git", branchName)
}
steps {
maven("test -Dproject.name=${project}/${branchName}")
}
}
}
job('parameterized-hello-world') {
parameters {
stringParam('MESSAGE', 'Hello world!')
}
properties {
rebuild {
autoRebuild()
}
}
steps {
shell('echo $MESSAGE')
}
}
Update job config.xml file
Example how to manipulate config.xml
Update git repository
for i in $(grep -rl artifactory.exmple.com *.xml); do sed -n 's/artifactory.exmple.com/artifactory1.exmple.cloud/p' ${i}; done
for i in $(grep -rl artifactory.exmple.com *.xml); do sed -i 's/artifactory.exmple.com/artifactory1.exmple.cloud/p' ${i}; done
Test
grep -lr gitlab.exmple.com * | sort | uniq | grep -v builds | while read line; do echo $line; sed -n 's/gitlab.exmple.com/gitlab.exmple.cloud/p' "$line" ; done
Change/substitute
grep -lr gitlab.exmple.com * | sort | uniq | grep -v builds | while read line; do echo $line; sed -i 's/gitlab.exmple.com/gitlab.exmple.cloud/' "$line" ; done
This requires Jenkins to reload configuration if the change was done outside of UI
java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -noCertificateCheck -s https://jenkins.example.com:8443/jenkins/ reload-configuration
-n quiet -i do change in line /p print