Java Garbage Collection
Analyse GC
Enable GC
Pass following parameters to starting java process
-XX:+PrintGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:"$CARBON_HOME/repository/logs/gc.log" -XX:+UseGCLogFileRotation -XX:NumberOfGCLogFiles=100 -XX:GCLogFileSize=1024K
Analyse
Use GCViewer
git clone https://github.com/chewiebug/GCViewer cd GCViewer mvn clean install java -jar ./target/gcviewer-1.36-SNAPSHOT.jar& #run in a background java -jar gcviewer-1.3x.jar gc.log.0;gc.log.1;gc.log.2;gc.log.current summary.csv [chart.png] [-t PLAIN|CSV|CSV_TS|SIMPLE|SUMMARY]
Recommended Throughput should be within 99% range.
Thread Dump
#!/bin/bash
# GIST: bsenduran/thread-analyze.sh
# https://gist.github.com/bsenduran/02e8bf024fcaaa7707a6bb2321e097a8
# If you get Permission Denied to connecto to process
# try to run just usr/lib/jvm/jdk-oracle/bin/jstack -F <javaPID>
# then rerun this script
# Other sources say you need to disable if you wish to use PTRACE()
# echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope #disables temporarly, default is "1"
# '-l' provides richer info, does not work on all OS, depends on Kernel config
if [ "$#" -ne 3 ]; then
echo "usage: sh thread-analyze.sh <pid> <number-of-dumps> <interval>"
echo " eg: sudo ./thread-analyze.sh 1632 3 10s"
echo "Avaialble units: s seconds, m for minutes, h for hours, d for days"
exit
fi
count=$2
for i in `seq 1 $count`;
do
/usr/lib/jvm/jdk-oracle/bin/jstack -F $1 > thread_dump_`date "+%F-%T"`.txt &
# /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-oracle/bin/jstack -F -l $1 > thread_dump_`date "+%F-%T"`.txt &
ps --pid $1 -Lo pid,tid,%cpu,time,nlwp,c > thread_usage_`date "+%F-%T"`.txt &
if [ $i -ne $count ]; then
echo "sleeping for $3 [$i]"
sleep $3
fi
done
Usage
sudo -u <user-of-PID> ./thread-analyze.sh <PID> <iterations> <delay-in-secons>s sudo -u <user-of-PID> ./thread-analyze.sh 1632 5 10s
JMX - Java Management Extensions
Connecting to the remote JVM is a two step process:
- First, the client will connect to the RMI registry to download the RMI stub for the JMXConnectorServer; this RMI stub contains the IP address and port to connect to the RMI server, i.e. the remote JMXConnectorServer.
- Second, the client uses the RMI stub to connect to the RMI server (i.e. the remote JMXConnectorServer) typically on an address and port that may be different from the RMI registry address and port.
The configuration for the RMI registry and the RMI server is specified by a JMXServiceURL. The string format of an RMI JMXServiceURL is:
service:jmx:rmi://<rmi_server_host>:<rmi_server_port>/jndi/rmi://<rmi_registry_host>:<rmi_registry_port>/jmxrmi
The RMI (Remote Method Invocation) is an API that provides a mechanism to create distributed application in java. The RMI allows an object to invoke methods on an object running in another JVM.
The RMI provides remote communication between the applications using two objects stub and skeleton.
References:
Jsonsole
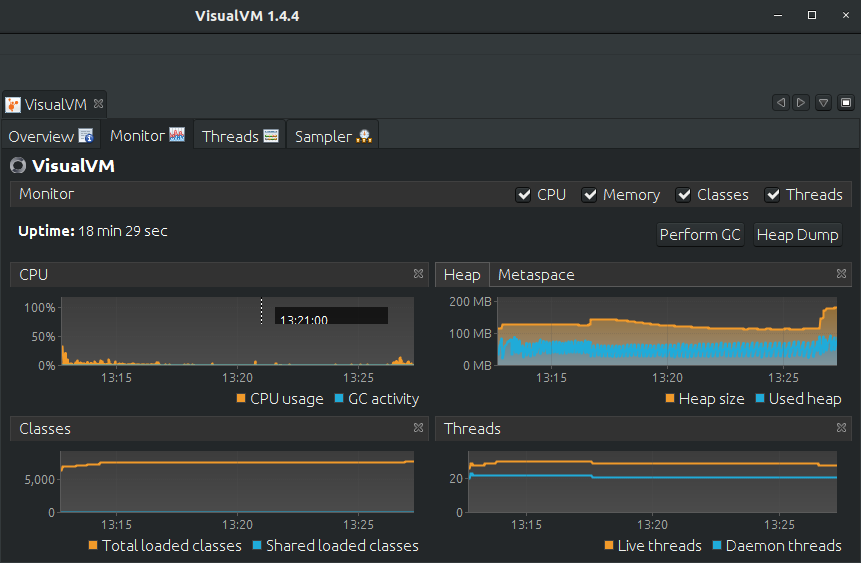
VisualVM
Modern replacement for Jconsole.
Collect heapdump
# get PID, remember ps -ef, where -f shows full command PID TTY TIME CMD 12631 ? 6-15:47:42 java # the following command should be run as a user of the process locate jmap # locate jmap location and if not in $PATH use full-path in the command below sudo -u <processID-user> jmap -dump:file=heap_dump.bin <process_Id> sudo -u <processID-user> jmap -dump:file=$(hostname)-<env>-$(date +"%Y%m%dT%H%M")-heap_dump.bin <process_Id>
Memory allocation
Java recommends heap of 25% of full memory for a container. It's 1/64 for initial and 1/4 for MAX.