Difference between revisions of "Kubernetes/Ingress controller"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
;Ingress vs Loadbalancer service | ;Ingress vs Loadbalancer service | ||
The difference between the LoadBalancer service and the Ingress in how the traffic routing is realized. In the case of the LoadBalancer service, the traffic that enters through the external load balancer is forwarded to the '''kube-proxy''' that in turn forwards the traffic to the selected pods. The '''Ingress load balancer''' forwards the traffic straight to the selected pods which is more efficient. | The difference between the LoadBalancer service and the Ingress in how the traffic routing is realized. In the case of the LoadBalancer service, the traffic that enters through the external load balancer is forwarded to the '''kube-proxy''' that in turn forwards the traffic to the selected pods. The '''Ingress load balancer''' forwards the traffic straight to the selected pods which is more efficient. | ||
= Ingress object = | |||
<source lang=yaml> | |||
# $ kubectl get ingresses ingress-with-auth -oyaml | |||
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 | |||
kind: Ingress | |||
metadata: | |||
annotations: | |||
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-realm: Authentication Required - foo | |||
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-secret: basic-auth | |||
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-type: basic | |||
name: ingress-with-auth | |||
namespace: default | |||
spec: | |||
rules: | |||
- host: echo-1.ingress.k8s.acme.cloud | |||
http: | |||
paths: | |||
- backend: | |||
serviceName: http-svc | |||
servicePort: 80 | |||
path: / | |||
status: | |||
loadBalancer: | |||
ingress: | |||
- ip: 172.17.0.2 # Kubernetes API server IP | |||
# public IP address on which this Ingress is available | |||
</source> | |||
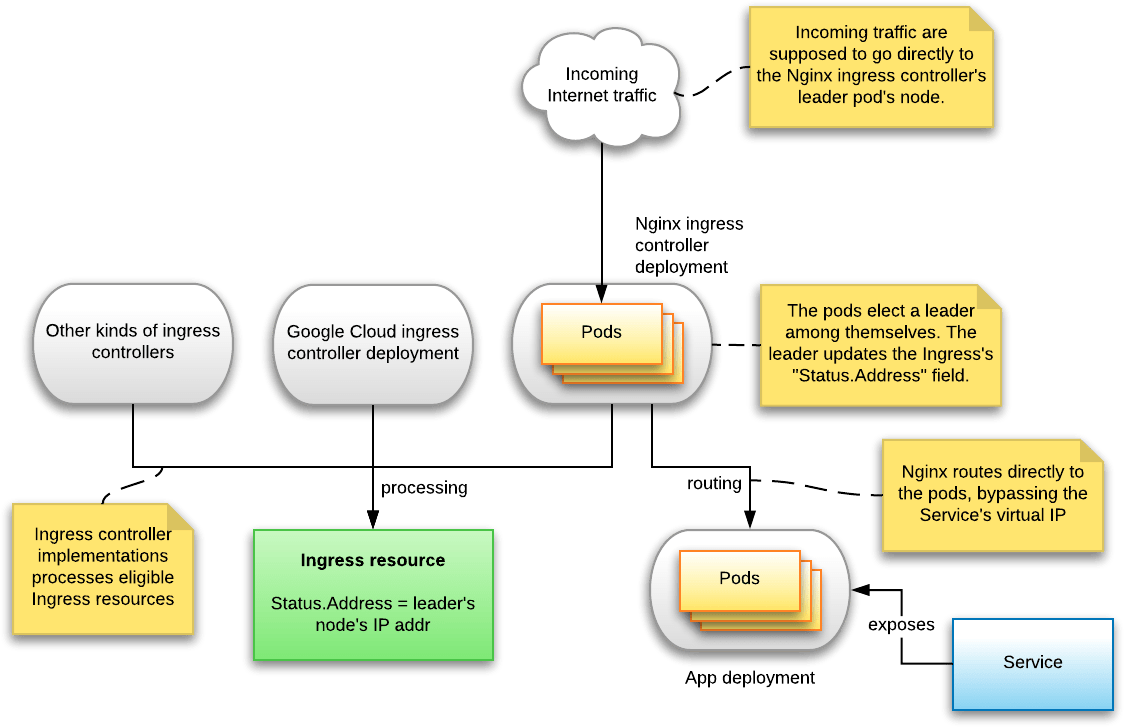
<code>Status.Address</code> update is a background goroutine that runs once a minute, queries the IP address of the node on which the Nginx ingress controller is running, and simply updates the <code>Status.Address</code> to that value. | |||
= [https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/examples/ Nginx ingress controller] = | = [https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/examples/ Nginx ingress controller] = | ||
:[[File:ClipCapIt-200611-143445.PNG]] | :[[File:ClipCapIt-200611-143445.PNG]] | ||
Revision as of 16:07, 11 June 2020
The Ingress resource type was introduced in Kubernetes version 1.1. The Kubernetes cluster must have an Ingress controller deployed in order for you to be able to create Ingress resources. What is the Ingress controller? The Ingress controller is deployed as a Docker container on top of Kubernetes. Its Docker image contains a load balancer like nginx or HAProxy and a controller daemon. The controller daemon receives the desired Ingress configuration from Kubernetes. It generates an nginx or HAProxy configuration file and restarts the load balancer process for changes to take effect. In other words, Ingress controller is a load balancer managed by Kubernetes.
- Ingress vs Loadbalancer service
The difference between the LoadBalancer service and the Ingress in how the traffic routing is realized. In the case of the LoadBalancer service, the traffic that enters through the external load balancer is forwarded to the kube-proxy that in turn forwards the traffic to the selected pods. The Ingress load balancer forwards the traffic straight to the selected pods which is more efficient.
Ingress object
# $ kubectl get ingresses ingress-with-auth -oyaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-realm: Authentication Required - foo
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-secret: basic-auth
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-type: basic
name: ingress-with-auth
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- host: echo-1.ingress.k8s.acme.cloud
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: http-svc
servicePort: 80
path: /
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- ip: 172.17.0.2 # Kubernetes API server IP
# public IP address on which this Ingress is available
Status.Address update is a background goroutine that runs once a minute, queries the IP address of the node on which the Nginx ingress controller is running, and simply updates the Status.Address to that value.
Nginx ingress controller
Nginx controller listens for events on the following resource types changes:
- Ingresses
- Endpoints
- Secrets
- ConfigMaps
Events get into the queue represented by controller.syncQueue and the internal/ingress/controller/controller.go queue handler function, function syncIngress(). This function collects all necessary information to regenerate the Nginx config file: it fetches all relevant Ingress objects and looks up associated Pods' IP addresses that the Ingresses should route to.
syncIngress() then calls internal/ingress/controller/nginx.go function OnUpdate() to actually write out the new Nginx config file and to reload Nginx.
Resources;
Resources
- Kubernetes Ingress Explained For Beginners by KodeKloud