Wireshark and Tshark
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
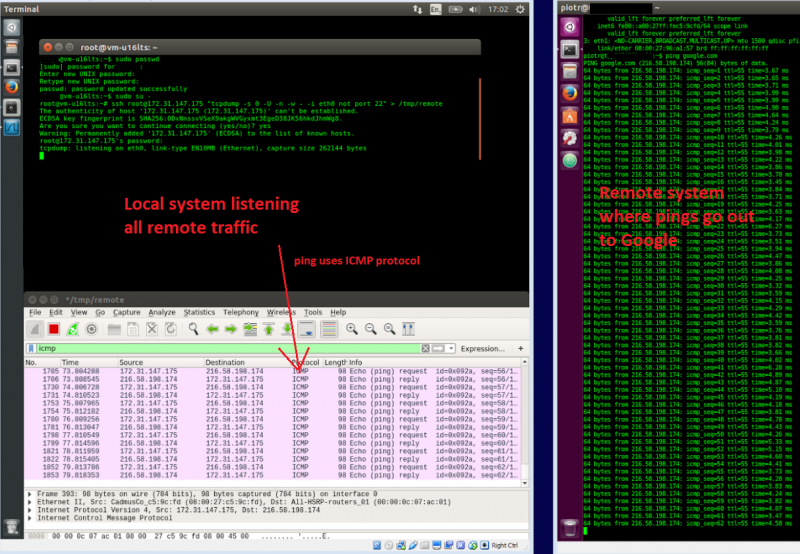
There are various ways to tap a Wireshark to a linux instance in order to observe live communication. Here below I am utilising named-pipes where tcpdump is redirecting its output to.
Prerequisites - Allow root SSH on Ubuntu Edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config to allow root password logins through ssh. As shown below, comment out #PermitRootLogin without-password and add PermitRootLogin yes.
# Authentication: LoginGraceTime 120 #PermitRootLogin without-password PermitRootLogin yes
Create named pipe on a system A where Wireshark is installed
sudo mkfifo /tmp/remote
Read from the pipe on system A to Wireshark
sudo wireshark -k -i /tmp/remote
Connect to system B as root user to a remote node then redirect tcpdump output to the named pipe over ssh to system A
ssh root@monior-this-host.com "tcpdump -s 0 -U -n -w - -i eth0 not port 22" > /tmp/remote
Filters
Operators
! - no, && - and, || - or
No STP, No Arp, No ipv6, no nbns, no DHCP
!stp && !arp && !ipv6 && !dhcpv6 && !nbns && !bootp.option.type == 53
Allow non-root (current) user to run tcpdump
#!/usr/bin/env bash # NOTE: This will let anyone who belongs to the 'pcap' group # execute 'tcpdump' # NOTE2: User running the script MUST be a sudoer. It is # convenient to be able to sudo without a password. sudo groupadd pcap sudo usermod -a -G pcap $USER sudo chgrp pcap /usr/sbin/tcpdump sudo setcap cap_net_raw,cap_net_admin=eip /usr/sbin/tcpdump sudo ln -s /usr/sbin/tcpdump /usr/bin/tcpdump