VLANs
VLAN setup
Basic VLANs info. Cisco series 1900 routers support up to 16 VLANs.
- Create
#vlan vlan_id
- Deleting a VLAN
#no vlan vlan_id
- Show all VLANs summary and port assignment
s1# show vlan brief !a switch command
r1# show vlan-switch !a router command
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Gi0/1/0, Gi0/1/1, Gi0/1/2
Gi0/1/3
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans2
---- ----- ---------- ----- ------ ------ -------- ---- -------- ------ ------
1 enet 100001 1500 - - - - - 1002 1003
1002 fddi 101002 1500 - - - - - 1 1003
1003 tr 101003 1500 1005 0 - - srb 1 1002
1004 fdnet 101004 1500 - - 1 ibm - 0 0
1005 trnet 101005 1500 - - 1 ibm - 0 0
Access port configuration
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 description Access Port to Cisco Access Point switchport access vlan 10 no ip address end
interface range
interface range gi 0/1/0 - 3
Trunk port configuration
For 802.1Q trunking, one VLAN is not tagged. This VLAN is called native VLAN. The native VLAN is used for untagged traffic when the port is in 802.1Q trunking mode. While configuring 802.1Q trunking, it is very important to keep in mind that the native VLAN must be configured the same on each side of the trunk link. It is a common mistake not to match the native VLANs while configuring 802.1Q trunking between the router and the switch.
In this example 802.1Q encapsulation is used
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
description Trunk Port to Cisco WLC
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk !changes to permanent trunking mode, the port enters into a Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) negotiation
!to convert the link into a trunk link even if the interface connecting to it does not agree to the change.
switchport trunk native vlan 99
switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10,20,99
switchport nonegotiate
no shutdown
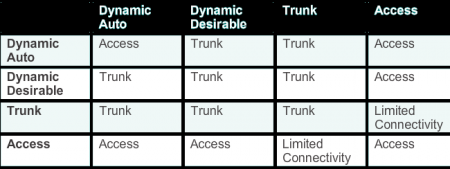
The following list shows options for the switchport mode command.
- trunk - configures the port into permanent 802.1Q trunk mode and negotiates with the connected device to convert the link to trunk mode.
- access - disables port trunk mode and negotiates with the connected device to convert the link to nontrunk.
- nonegotiate - the port is a trunk and does not do DTP negotiation with the other side of the link.
- dynamic desirable - triggers the port to negotiate the link from nontrunk to trunk mode. The port negotiates to a trunk port if the connected device is in trunk state, desirable state, or auto state. Otherwise, the port becomes a nontrunk port.
- dynamic auto - enables a port to become a trunk only if the connected device has the state set to trunk or desirable. Otherwise, the port becomes a nontrunk port.
Verifying a Trunk
switch# show interfaces trunk !can be issued on a router or switch Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Gi0/1/0 on 802.1q trunking 99 Gi0/1/1 on 802.1q trunking 99 Gi0/1/2 on 802.1q trunking 99 Gi0/1/3 on 802.1q trunking 99 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Gi0/1/0 1,10,20,99,1002-1005 Gi0/1/1 1,10,20,99,1002-1005 Gi0/1/2 1,10,20,99,1002-1005 Gi0/1/3 1,10,20,99,1002-1005 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Gi0/1/0 1,10,20,99 Gi0/1/1 1,10,20,99 Gi0/1/2 1,10,20,99 Gi0/1/3 1,10,20,99 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Gi0/1/0 1,10,20,99 Gi0/1/1 1,10,20,99 Gi0/1/2 1,10,20,99 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Gi0/1/3 1,10,20,99
Switch# show interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport Switch# show interfaces GigabitEthernet1/0/1 trunk
DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol)
DTP is used to automatically form a trunk between switches. Default DTP setting is dependent on the IOS software version and platform used. DTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. Therefore some network devices might forward DTP frames improperly, which can cause misconfigurations. To avoid this, turn off DTP on interfaces on a Cisco switch connected to devices that do not support DTP/connected to 3rd party hardware.
The operation of DPT can be verified by issuing show dtp interface. Output below shows that Trunk Operational Status (TOS) is set to trunk, Trunk Administrative Status (TAS) is desirable, and Trunk Negotiation Status (TNS) is also set to trunk. Trunk Operational Type (TOT), Trunk Adminstrative Type (TAT), and Trunk Negotiation Type (TNT) show 802.1q encapsulation. Output below is from Cisco 1941 IOS Version 15.2(4)M4 with EHWIC-4ESG-P Ether-switch card that does not support DTP. Therefore the output you can see 'NONEGOTIATE' and timers with zero.
Switch#show dtp interface Gi0/1/0 DTP Interface Information: TOS/TAS/TNS: TRUNK/NONEGOTIATE/TRUNK TOT/TAT/TNT: 802.1Q/802.1Q/802.1Q Neighbor address 1: 000000000000 Neighbor address 2: 000000000000 Hello timer expiration ms/state: 0/STOPPED Access timer expiration ms/state: 0/STOPPED Negotiation timer expiration ms/state: 0/STOPPED Multidrop timer expiration ms/state: 0/STOPPED FSM state: S6:TRUNK # times multi & trunk: 0 Enabled: 1 In STP: 0
- trunk - automatically enables trunking regardless of the state of the neighboring switch and regardless of any DTP requests that are sent from the neighboring switch.
- access - trunking is not allowed on this port regardless of the state of the neighboring switch interface and regardless of any DTP requests that are sent from the neighboring switch.
- nonegotiate - prevents the interface from generating DTP frames. This command can be used only when the interface switch port mode is access or trunk. You must manually configure the neighboring interface as a trunk interface to establish a trunk link.
- dynamic desirable - communicates to the neighboring switch via DTP that the interface is attempting to become a trunk if the neighboring switch interface is able to become a trunk.
- dynamic auto - creates the trunk based on the DTP request from the neighboring switch. Interface will become a trunk interface if the neighboring iface is set to trunk or desirable mode
- Nonegotiate mode operation
The switchport nonegotiate interface command stops DTP negotiation packets sending and engaging in trunk election. This command is valid only when the interface switch port mode is access or trunk. This command returns an error if you attempt to execute it in dynamic (auto or desirable) mode. When in nonegotiate configuration, the port trunks only if the other end of the link is specifically set to trunk. The switchport nonegotiate command does not form a trunk link with ports in either dynamic desirable or dynamic auto mode.
Native VLAN
- Tagged Frames on the Native VLAN - are discarded
Some devices that support trunking, add a VLAN tag to native VLAN traffic. Control traffic sent on the native VLAN should not be tagged. If an 802.1Q trunk port receives a tagged frame with the VLAN ID the same as the native VLAN, it drops the frame. Consequently, when configuring a switch port on a Cisco switch, configure devices so that they do not send tagged frames on the native VLAN. Devices from other vendors that support tagged frames on the native VLAN include IP phones, servers, routers, and non-Cisco switches.
- Untagged Frames on the Native VLAN
When a Cisco switch trunk port receives untagged frames (which are unusual in a well-designed network), it forwards those frames to the native VLAN. If there are no devices associated with the native VLAN (which is not unusual) and there are no other trunk ports (which is not unusual), then the frame is dropped. The default native VLAN is VLAN 1. When configuring an 802.1Q trunk port, a default Port VLAN ID (PVID) is assigned the value of the native VLAN ID. All untagged traffic coming in or out of the 802.1Q port is forwarded based on the PVID value. For example, if VLAN 99 is configured as the native VLAN, the PVID is 99 and all untagged traffic is forwarded to VLAN 99. If the native VLAN has not been reconfigured, the PVID value is set to VLAN 1.
Troubleshooting
- Lack of connectivity - missing VLAN
- Make sure your devices have correct ip addresses in correct subnets
- Check whether ports are a members of the correct VLAN
show vlan - Issue
show interfaces switchportand search for Inactive means that the VLAN has been deleted from vlan.dat file and needs recreating. This is because each port in a switch belongs to a VLAN.
- Trunk link troubleshooting
- Native VLAN check - use
show interfaces trunkat both ends to check whether a native VLAN matches on both sites. If not VLAN leaking occurs meaning that port can accept frames form a different VLAN that is assigned to. If CDP is enabled it will display %CDP-4-NATIVE_VLAN_MISMATCH message.
In a native VLAN mismatch scenario connectivity issues occur in the network if a native VLAN mismatch exists. Data traffic for VLANs, other than the two native VLANs configured, successfully propagates across the trunk link, but data associated with either of the native VLANs does not successfully propagate across the trunk link. - Trunk status - use
show interfaces trunkat both ends. If possible configure interfaces to trunk mode. Cisco Catalyst switch ports use DTP by default and attempt to negotiate a trunk link. - Allowed VLANs on trunk - use
show interfaces trunkto see allowed VLANs on the trunk link. There can be missing or not allowed VLAN causing the problem.
Security - control traffic
All control traffic is sent on VLAN 1. Therefore, when the native VLAN is changed to something other than VLAN 1, all control traffic is tagged on IEEE 802.1Q VLAN trunks (tagged with VLAN ID 1). A recommended security practice is to change the native VLAN to a different VLAN than VLAN 1.