Kubernetes/Kustomize
Kustomize
- kubectl+kustomize SIG CLI
kustomize lets you customize raw, template-free YAML files for multiple purposes, leaving the original YAML untouched and usable as is.
Install
# Detects your OS and downloads kustomize binary to cwd
curl -s "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/master/hack/install_kustomize.sh" | bash
# Install on Linux - option2
VERSION=v4.1.2
VERSION=$(curl --silent "https://api.github.com/repos/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases" | jq -r '.[].tag_name | select(. | contains("kustomize"))' | sort | tail -1 | cut -d"/" -f2); echo $VERSION
curl -L https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/releases/download/kustomize%2F${VERSION}/kustomize_${VERSION}_linux_amd64.tar.gz -o kustomize_${VERSION}_linux_amd64.tar.gz
tar xzvf kustomize_${VERSION}_linux_amd64.tar.gz
sudo install ./kustomize /usr/local/bin/kustomize
kustomize version --short
{kustomize/v4.1.2 2021-04-15T20:38:06Z }
Kustomize build workflow
- kustomize vars - use
envsubstinstead
$ kustomize build ~/target
- load universal k8s object descriptions
- read
kustomization.yamlfrom target - kustomize bases (recurse 2-5)
- load and/or generate resources
- apply target's kustomization operations
- fix name references
- emit yaml
= kustomize.yaml
A build stage first
- processes resources,
- then it processes generators, adding to the resource list under consideration,
- then it processes transformers to modify the list,
- and finally runs validators to check the list for whatever error.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- {pathOrUrl}
- what resources you want to customize
# cross-cutting fields
namespace: custom
namePrefix: dev-
nameSuffix: "-svc"
commonLabels:
app: web
commonAnnotations:
value: app
generators:
- {pathOrUrl}
- what new resources should be created.
generatorOptions:
disableNameSuffixHash: true
labels:
env: prod
annotations:
app: custom
transformers:
- {pathOrUrl}
- what to transform in above mentioned resources
validators:
- {pathOrUrl}
- ...
Patches
- patchStrategicMerge
- Kubernetes supports a customized version of JSON merge patch called strategic merge patch. This patch format is used by
kubectl apply,kubectl editandkubectl patch, and contains specialized directives to control how specific fields are merged.
Example 101
Note: Bases have been deprecated in v2.1.0 resources-expanded-bases-deprecated
- Kustomize builder note that it operates on the 1st yaml document
| base/kustomization.yaml | overlays/dev/kustomization.yaml | overlays/prod/kustomization.yaml |
|---|---|---|
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization commonLabels: app: sonarqube resources: - gateway.yaml - virtual-service.yaml |
apiVersion: ... kind: Kustomization patches: - gateway_patch.yaml - virtual-service_patch.yaml resources: - ../../base |
apiVersion: ... kind: Kustomization patches: - gateway_patch.yaml - virtual-service_patch.yaml resources: - ../../base |
.
├── base
│ ├── gateway.yaml
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ └── virtual-service.yaml
└── overlays # more contextual this directory could be called 'environments'
├── dev
│ ├── gateway_patch.yaml
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ └── virtual-service_patch.yaml
└── prod
├── gateway_patch.yaml
├── kustomization.yaml
└── virtual-service_patch.yaml
# Build kuctomized output
kustomize version --short # -> {kustomize/v3.8.2 2020-08-29T17:44:01Z }
kustomize build overlays/dev # apply patches
kustomize build base # run common functions (as described in base/kustomize.yaml) against the whole code base
What happens?
kustomize build overlays/devfindskustomization.yaml, that describes:patches: [gateway_patch.yaml, virtual-service_patch.yaml]to be used over the baseresources: [../../base]. There are 3 type of patches: patches, patchesStrategicMerge, patchesJson6902 to choose from
overlays/dev/kustomization.yamlcascades to the base (source of manifests to be changed) via directiveresources: ["../../base"]- The base directory contains and runs its own
kustomization.yamlfile. - The
base/kustomization.yamlcontains common operations, eg.commonLabels, namePrefixfunctions to be applied to whole code base. - Then patch file(s) are applied eg.
gateway_patch.yamlcontains enough information to identify a resource/object and apply changes.
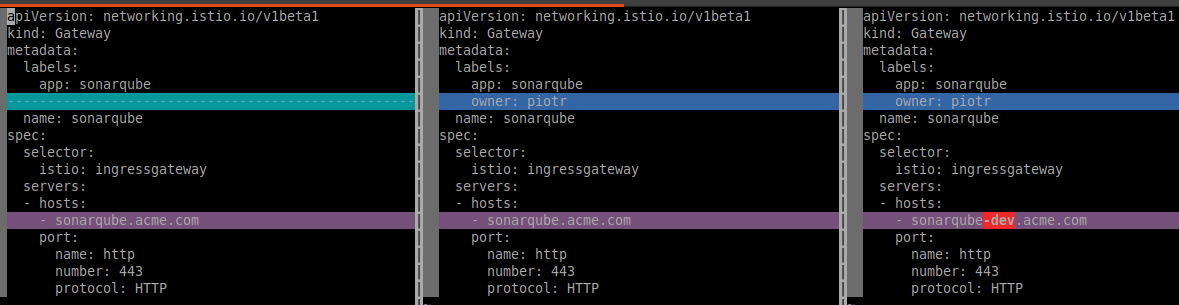
So, what happens
# Applying the patch: overlays/dev/gateway_patch.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: sonarqube
spec:
servers:
- port:
number: 443
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- sonarqube-dev.acme.com # <- override
# |
# | over the base
# v
# base/gateway.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
labels:
app: sonarqube
name: sonarqube
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- hosts:
- sonarqube.acme.com
port:
name: http
number: 443
protocol: HTTP
# |
# | results with
# v
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
labels:
app: sonarqube
owner: piotr # <- label added by base kustomize.yaml fn
name: sonarqube
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- hosts:
- sonarqube-dev.acme.com # <- patch override
port:
name: http
number: 443
protocol: HTTP
Check yourselves
# __unchanged manifest_ _base kustomization_ ___patch overlay____________ vimdiff <(cat base/gateway.yaml) <(kustomize build base) <(kustomize build overlays/dev)
Cheatsheet
Patch multiple objects
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ../base
patches:
- path: patch.json
target:
kind: PersistentVolume
version: v1
group: ""
name: volume-(data|master)-\d # regex match
labelSelector: |
app.kubernetes.io/component=storage,
app.kubernetes.io/name=elasticsearch
Delete an object from the base
Strategic Merge Patch provides some patch options like replace, merge, and delete. The simple 'patch' can only patch (manipulate) it.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ../base
patchesStrategicMerge:
- |-
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: unwanted-namespace
$patch: delete
secretGenerator
Secrets can be generated from environment variables. Within a template file there is a list of variables, where the variable will become a key and it's value the value.
Environment variable secret template
GIT_USERNAME GIT_PASSWORD GIT_CREDENTIALS
Kustomization
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
secretGenerator:
- name: argocd-git-secret
envs:
- git.env
options:
disableNameSuffixHash: true
Known issues
- commonLabels altering podSelector.matchLabels and Allow excluding some label selectors from commonLabels
In some settings it makes sense for commonLabels to be included in selectors, and in some settings it doers not make sense to include them in selectors. Kustomize includes by default, and there is no way to opt out. As workaround, you can convert matchLabels to matchExpressions and Kustomize won't touch them. API docs
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: mongodb-backup
is equivalent with
- podSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- mongodb-backup
and Kustomize will keep its hands off.