Difference between revisions of "IPv6 network addresses"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
= Unicast IPv6 addresses = | = Unicast IPv6 addresses = | ||
*'''Global unicast''' - similar to a public IPv4 address. These are globally unique, Internet routable addresses. Global unicast addresses can be configured statically or assigned dynamically. | *'''Global unicast''' - similar to a public IPv4 address. These are globally unique, Internet routable addresses. Global unicast addresses can be configured statically or assigned dynamically. | ||
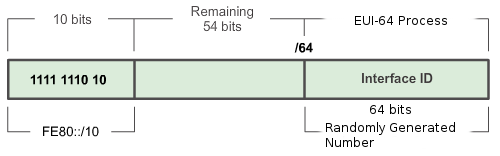
*'''Link-local''' - Link-local addresses are used to communicate with other devices on the same local link. With IPv6, the term link refers to a subnet. Link-local addresses are confined to a single link. Their uniqueness must only be confirmed on that link because they are not routable beyond the link. In other words, routers will not forward packets with a link-local source or destination address. They are from <span style="color: orange">'''FE80::/10'''</span> range | *'''Link-local''' - Link-local addresses are used to communicate with other devices on the same local link. With IPv6, the term link refers to a subnet. Link-local addresses are confined to a single link. Their uniqueness must only be confirmed on that link because they are not routable beyond the link. In other words, routers will not forward packets with a link-local source or destination address. They are from <span style="color: orange">'''FE80::/10'''</span> range and also used by IPv6 routing protocols to exchange messages and as the next-hop address in the IPv6 routing table. | ||
[[File:Ipv6_link-local_address.png|none|left|Ipv6_link-local_address]] | [[File:Ipv6_link-local_address.png|none|left|Ipv6_link-local_address]] | ||
*'''Loopback''' - represented as <span style="color: orange">'''::1/128'''</span> or just <span style="color: orange">'''::1'''</span> in the compressed format | *'''Loopback''' - represented as <span style="color: orange">'''::1/128'''</span> or just <span style="color: orange">'''::1'''</span> in the compressed format | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 15 November 2014
There are three types of IPv6 addresses:
- Unicast - An IPv6 unicast address uniquely identifies an interface on an IPv6-enabled device.
- Multicast - An IPv6 multicast address is used to send a single IPv6 packet to multiple destinations.
- Anycast - An IPv6 anycast address is any IPv6 unicast address that can be assigned to multiple devices. A packet sent to an anycast address is routed to the nearest device having that address.
IPv6 does not have a broadcast address. However, there is an IPv6 all-nodes multicast address that essentially gives the same result.
Unicast IPv6 addresses
- Global unicast - similar to a public IPv4 address. These are globally unique, Internet routable addresses. Global unicast addresses can be configured statically or assigned dynamically.
- Link-local - Link-local addresses are used to communicate with other devices on the same local link. With IPv6, the term link refers to a subnet. Link-local addresses are confined to a single link. Their uniqueness must only be confirmed on that link because they are not routable beyond the link. In other words, routers will not forward packets with a link-local source or destination address. They are from FE80::/10 range and also used by IPv6 routing protocols to exchange messages and as the next-hop address in the IPv6 routing table.
- Loopback - represented as ::1/128 or just ::1 in the compressed format
- Unspecified address - ::/128 or just :: in the compressed format. It cannot be assigned to an interface and is only be used as a source address. It is used as a source address when the device does not yet have a permanent IPv6 address or when the source of the packet is irrelevant to the destination.
- Unique local - some similarity to RFC 1918 private addresses for IPv4, Unique local addresses are used for local addressing within a site or between a limited number of sites. These addresses should not be routable in the global IPv6. Unique local addresses are in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7.
- IPv4 embedded - used to help transition from IPv4 to IPv6