Fibre optic DWDM
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
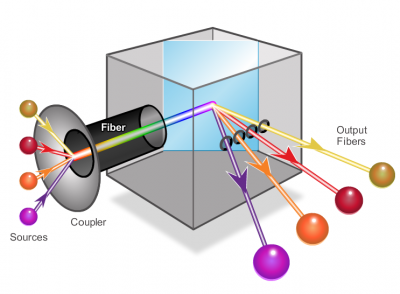
A newer fiber optic media development for long-range communications is called dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM). DWDM multiplies the amount of bandwidth that a single strand of fiber can support.
Specifically, DWDM:
- Enables bidirectional communications over one strand of fiber.
- Can multiplex more than 80 different channels of data (i.e., wavelengths) onto a single fiber.
- Each channel is capable of carrying a 10 Gb/s multiplexed signal.
- Assigns incoming optical signals to specific wavelengths of light (i.e., frequencies).
- Can amplify these wavelengths to boost the signal strength.
- Supports SONET and SDH standards.
Standards:
SONET is an American-based ANSI standard, while SDH is a European-based ETSI and ITU standard. Both are essentially the same and, therefore, often listed as SONET/SDH.
References
- Google DWDM search amazing
- Wavelength-division multiplexing Global Wiki
- ADVA used by BT customer premises equipment