AWS/Networking
Subnets
- Public subnet
If a subnet’s default traffic is routed to an internet gateway, the subnet is known as a public subnet. For example, an instance launched in this subnet is publicly accessible if it has an Elastic IP address or a public IP address associated with it.
- Private subnet
If a subnet's default traffic is routed to a NAT instance/gateway or completely lacks a default route, the subnet is known as a private subnet. For example, an instance launched in this subnet is not publicly accessible even if it has an Elastic IP address or a public IP address associated with it.
Peerlink - unsupported configurations
Peerlinks are not transitive - use Transit Gateway for this. The reason seems to be historical, that Peerlink connections allow you to link overlapping CIDR ranges eg.
- VPC-A 10.0.0.0/16
- VPC-B 192.168.1.0/24
- VPC-C 192.168.1.0/24
Allow you peerlink VPC-B <--> VPC-A <--> VPC-C. Of course VPC-B does not have direct connection to VPC-C.
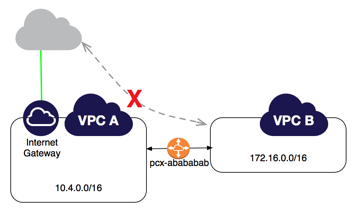
- Edge to Edge Routing Through a Gateway or Private Connection
If either VPC in a peering relationship has one of the following connections, you cannot extend the peering relationship to that connection:
- A VPN connection or an AWS Direct Connect connection to a corporate network
- An internet connection through an internet gateway
- An internet connection in a private subnet through a NAT device
- A VPC endpoint to an AWS service; for example, an endpoint to Amazon S3.
Edge to Edge Routing Through a VPN Connection or an AWS Direct Connect Connection
Edge to Edge Routing Through an InternetGateway