Linux monitor resources from terminal
Resources
mtr - My Traceroute
Combines ping and traceroute into interactive tool. It's often already included in the most of distributions.
Usage:
$ mtr wp.pl
Key bindings:
- d - to switch Display modes:
- tracert+ping,
- Cisco lost packets
- Latency
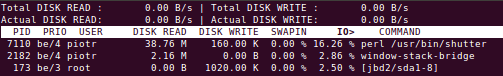
iotop
$sudo iotop -aoP
- -a Will show accumulated output
- -o Will only output
- -P Will only show processes instead of threads
sysstat
sudo apt-get install sysstat
$ sar 09:25:01 AM CPU %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle 09:35:01 AM all 0.11 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 99.88 09:45:01 AM all 0.12 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 99.86
The %iowait is the time spent waiting on I/O. Using the Debian package, you must enable the stat collector via the /etc/default/sysstat config file after package installation. To see current utilization broken out by device, you can use the iostat
$sudo iostat -x 1
Linux 3.13.0-43-generic (piotr-x220) 21/05/15 _x86_64_ (4 CPU)
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
4.37 0.03 17.66 3.68 0.00 74.26
Device: rrqm/s wrqm/s r/s w/s rkB/s wkB/s avgrq-sz avgqu-sz await r_await w_await svctm %util
sda 8.23 39.52 78.63 45.53 3546.76 4702.75 132.88 6.22 50.06 9.87 119.45 3.09 38.37
dstat
$ sudo apt-get install dstat
$ dstat -tdD total,sda,sdb,sdc,md1 60 #colourful
----system---- -dsk/total----dsk/sda--
time | read writ: read writ
21-05 22:13:04|3441k 4478k:3441k 4478k
21-05 22:13:18| 109k 242k: 109k 242k
21-05 22:13:29| 62k 1404k: 62k 1404k
21-05 22:13:34| 81k 1263k: 81k 1263k
- -t for timestamps
- -d for disk statistics
- -D to specify the exact devices to report
- 60 to average over 60 seconds. The display is updated every second, but only once per 60 seconds a new line will be started.
- -c can report wait IO percentage, which in most cases is related to the CPU waiting for data from the disks
Saidar
sudo apt-get install saidar Hostname : linux-ubuntu Uptime : 00:14:52 Date : 2015-01-25 11:56:42 Load 1 : 0.19 CPU Idle : 96.01% Running : 2 Zombie : 0 Load 5 : 0.27 CPU System: 1.12% Sleeping : 198 Total : 200 Load 15 : 0.22 CPU User : 2.87% Stopped : 0 No. Users : 2 Mem Total : 3729M Swap Total: 3869M Mem Used : 22.04% Paging in : 0 Mem Used : 822M Swap Used : 0B Swap Used : 0.00% Paging out: 0 Mem Free : 2907M Swap Free : 3869M Total Used: 10.82% Disk Name Read Write Network Interface rx tx ram0 0B 0B eth0 0B 0B ram1 0B 0B lo 0B 0B ram2 0B 0B wlan0 373B 84B ram3 0B 0B ram4 0B 0B Mount Point Free Used ram5 0B 0B / 245G 10.59% ram6 0B 0B /sys 0B -nan% ram7 0B 0B /proc 0B -nan% ram8 0B 0B /dev 1854M 0.00% ram9 0B 0B /dev/pts 0B -nan% ram10 0B 0B /run 371M 0.34% ram11 0B 0B / 245G 10.59%
Glances also shows containers
Written in Python and light on resources text based and API aware monitoring tool
$ curl -L https://bit.ly/glances | /bin/bash $ wget -O- https://bit.ly/glances | /bin/bash $ pip install glances
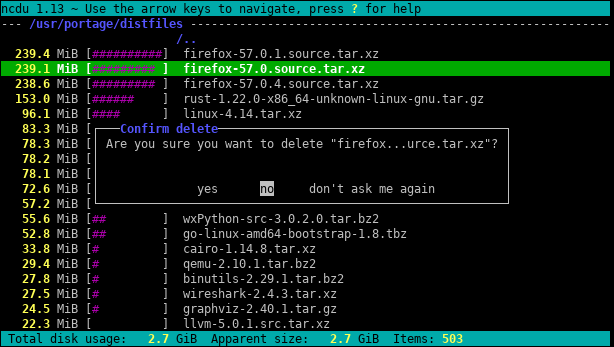
Ncdu - NCurses Disk Usage
Ncdu is a disk usage analyzer with an ncurses interface.
sudo apt install ncdu
Key bindings:
e - show hidden files
g - show %
i - show info
r - rescan
b - spawn shell
s - sort by size
n - sort by name
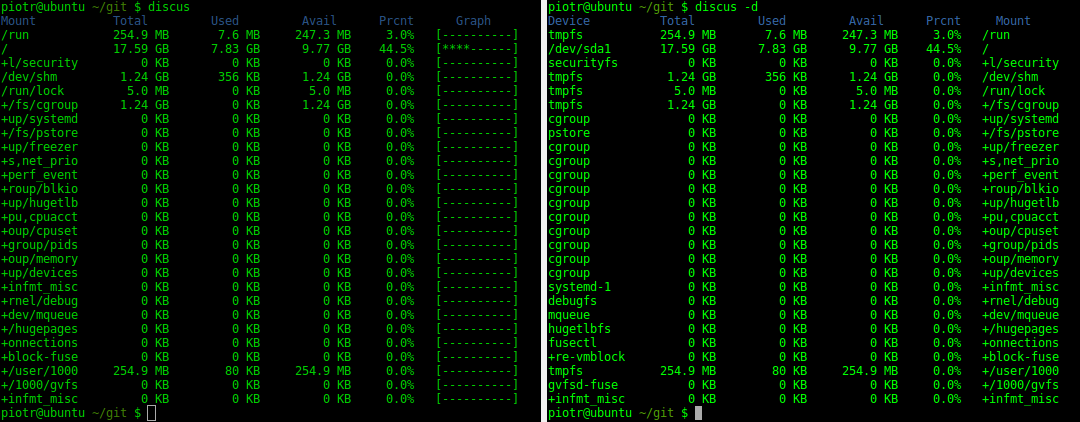
Discus - Disk Space Usage
sudo apt install discus #Debian/UBuntu, it takes ~60kB sudo yum install discus #RHEL/CentOS sudo dnf install discus #Fedora 22+
Network
verify check tcp port open
No nc, or any other tools, you can check verify tcp open socket using Linux native /dev/tcp device.
$> </dev/tcp/localhost/22 && echo port-open || echo port-closed $> </dev/tcp/10.244.2.2/80 && echo port-open || echo port-closed $> </dev/tcp/k8sservice/80 && echo port-open || echo port-closed
netstat - network statistics
In CentOS 7 net-tools package has been replaced by iproute2 therefore in course to use netstat needs installing:
[piotr@vmcent7 ~]$ sudo yum install net-tools $ sudo netstat -pant Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1771/master tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1434/sshd tcp 0 0 192.168.1.148:22 192.168.1.89:40653 ESTABLISHED 35910/sshd: piotr [ tcp 0 0 192.168.1.148:22 192.168.1.89:40614 ESTABLISHED 35831/sshd: piotr [ tcp 0 0 192.168.1.148:22 192.168.1.64:4334 ESTABLISHED 35679/sshd: piotr [ tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1771/master tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1434/sshd
Show UDP, notice switch -u used to show only UDP protocol
$ netstat -anup udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:514 0.0.0.0:* 3111/rsyslogd udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:42528 0.0.0.0:* 3111/rsyslogd udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:33498 0.0.0.0:* 3111/rsyslogd udp 0 0 :::514 :::* 3111/rsyslogd
ss - socket viewer
ss tool is by defult shipped in a minimal CentOS 7, similar to the netstat provides more detailed information about sockets.
$ sudo ss -pant
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* users:(("master",1771,13))
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* users:(("sshd",1434,3))
ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.148:22 192.168.1.89:40653 users:(("sshd",35914,3),("sshd",35910,3))
ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.148:22 192.168.1.89:40614 users:(("sshd",35835,3),("sshd",35831,3))
ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.148:22 192.168.1.64:4334 users:(("sshd",35683,3),("sshd",35679,3))
LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::* users:(("master",1771,14))
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::* users:(("sshd",1434,4))
Show UDP ports
$ ss -a -A udp -n #or ss -luna State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port UNCONN 0 0 *:55040 *:* UNCONN 10600 0 *:514 *:* UNCONN 0 0 *:34827 *:* UNCONN 0 0 *:43157 *:* UNCONN 0 0 *:52377 *:* ESTAB 0 0 127.0.0.1:35869 127.0.0.1:35869
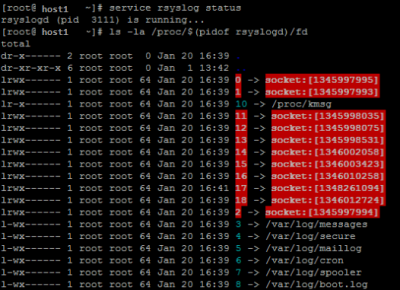
Show Unix SOCKETS
$ ls -la /proc/$(pidof rsyslog)/fd
tcptrack
apt-get install tcptrack tcptrack -i <interface> tcptrack -i eth0 "dst port 80"
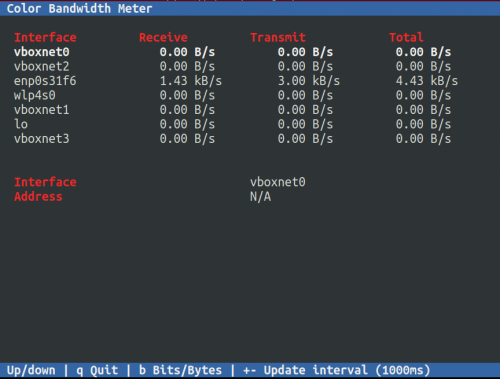
CBM Color Bandwidth Meter
The Color Bandwidth Meter (CBM) is a small program to display the traffic currently flowing through the network devices in a simple curses-based GUI. The traffic for all interfaces include values as receive, transfer and total Bytes/s or bits/s (or its multiples as KB/s and Kb/s).
sudo apt install cbm
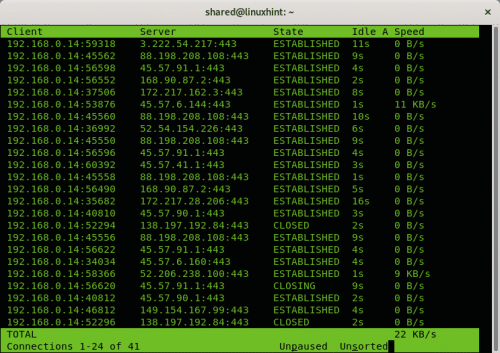
Pktstat
Pktstat displays all the active connections in real time, and the speed at which data is being transferred through them. It also displays the type of the connection, i.e. tcp or udp and also details about http requests if involved.
$ sudo pktstat -i eth0 -nt
nload - network load
apt-get install nload # Ubuntu 22.04 docker image nload # use left right arrow to switch view between interfaces
sar -n KEYWORD <every_sec> <count> - report network statistics
This reports various network statistics. For example: number of packets received (transmitted) through the network card, statistics of packet failure etc.,. “1 3” reports for every 1 seconds a total of 3 times.
$ sar -n DEV 1 10
KEYWORD can be one of the following:
- DEV – Displays network devices vital statistics for eth0, eth1, etc.,
- EDEV – Display network device failure statistics
- NFS – Displays NFS client activities
- NFSD – Displays NFS server activities
- SOCK – Displays sockets in use for IPv4
- IP – Displays IPv4 network traffic
- EIP – Displays IPv4 network errors
- ICMP – Displays ICMPv4 network traffic
- EICMP – Displays ICMPv4 network errors
- TCP – Displays TCPv4 network traffic
- ETCP – Displays TCPv4 network errors
- UDP – Displays UDPv4 network traffic
- SOCK6, IP6, EIP6, ICMP6, UDP6 are for IPv6
- ALL – This displays all of the above information. The output will be very long.
dnstop - domain queries stats
./dnstop eth0 #download http://dnstop.measurement-factory.com
Available statistics can be toggled using key shortcuts
Query Type Count % ---------- --------- ------ A? 202 97.1 NS? 4 1.9 SRV? 1 0.5 AAAA? 1 0.5 Source Query Name Count % Destinations Count % ----------- ---------- --------- ------ ------------ --------- ------ 10.0.20.197 com 106 46.1 195.60.0.5 173 67.8 10.0.20.197 net 106 46.1 195.60.0.1 82 32.2 10.0.20.197 uk 8 3.5 .. 2nd level Query Names TopLevelDomain - queries Query Name Count % Query Name Count % ---------------- --------- ------ ---------- --------- ------ akamaiedge.net 5 38.5 net 38 73.1 akamai.net 3 23.1 com 12 23.1 adobe.com 1 7.7d? . 1 1.9 twitter.com 1 7.7 uk 1 1.9 ..
Key shortcuts
s - Sources list t - Query types r - Rcodes ^R - Reset counters d - Destinations list o - Opcodes ^X - Exit 1 - 1st level Query Names ! - with Sources 2 - 2nd level Query Names @ - with Sources 3 - 3rd level Query Names # - with Sources 4 - 4th level Query Names $ - with Sources 5 - 5th level Query Names % - with Sources 6 - 6th level Query Names ^ - with Sources 7 - 7th level Query Names & - with Sources 8 - 8th level Query Names * - with Sources 9 - 9th level Query Names ( - with Sources
Hardware
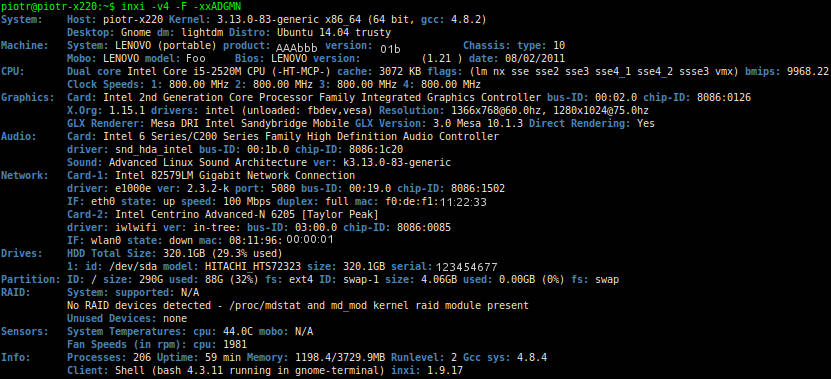
inxi
inxi -v4 -F -xxADGMN
List of resource monitoring tools
- Performance and resources monitors
- ctop top for containers
- htop
- lsof
- iotop
- vmstat -S m #displays stats in Mb
- glances
- Bootup time
- systemd-analyze blame
- systemd-analyze critical-chain
- systemd-analyze plot > boot_analysis.svg; xviewer boot_analysis.svg
- Web servers
- ngxtop -monitor nGinx logs/count/responses
- SSL
- sslscan
- testssl.sh
- Network monitoring tools
- bmon
- bwbar
- bwm
- bwm-ng
- iftraf
- iftop
- iperf
- ipfm
- speedometer
- cbm
- ibmonitor
- pktstat
- mactrack
- nload -u K wlan0
- vnstat -d -i wlan0
- sudo tcptraceroute
- trace 198.6.1.2
- traceroute
- tracepath
- tracepath6
- mtr 198.6.1.2
- ngrep -searches network streams, it's tcpdump compatible syntax
- Space utilization
- ncdu
- discus
- dutree
- Hardware
- lspci
- inxi -v4 -F -xxADGMN
- Logs
- lnav
- multitail
- journalctl -systemd tool
Network statistics scripts
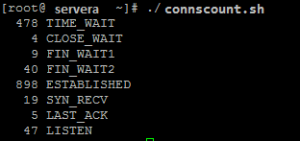
connscount.sh
#!/bin/bash
netstat -an | awk '/^tcp/ {A[$(NF)]++} END {for (I in A) {printf "%5d %s\n", A[I], I}}'
dnscheck.pl
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
use strict;
while () {
my $date = localtime(time());
open(CH,"dig \@195.60.0.1 www.bbc.co.uk |") || die "cannot run dig: $!\n";
while (<CH>) {
chomp;
next unless /query time/i;
print $date . "$_\n";
};
close CH;
open(CH,"dig \@195.60.0.5 www.bbc.co.uk |") || die "cannot run dig: $!\n";
while (<CH>) {
chomp;
next unless /query time/i;
print $date . "$_\n";
};
close CH;
sleep 10;
};
Run
./dnscheck.pl Fri Dec 11 21:50:15 2015;; Query time: 5 msec Fri Dec 11 21:50:15 2015;; Query time: 4 msec
Service control managers
- Ubuntu: System > Administrator > services
- bum - GUI bootup manager
- rcconf
- sysv-rc-conft