Fibre optic DWDM
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
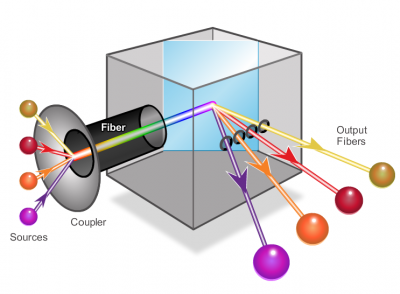
A newer fiber optic media development for long-range communications is called dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM). DWDM multiplies the amount of bandwidth that a single strand of fiber can support.
Specifically, DWDM:
- Enables bidirectional communications over one strand of fiber.
- Can multiplex more than 80 different channels of data (i.e., wavelengths) onto a single fiber.
- Each channel is capable of carrying a 10 Gb/s multiplexed signal.
- Assigns incoming optical signals to specific wavelengths of light (i.e., frequencies).
- Can amplify these wavelengths to boost the signal strength.
- Supports SONET and SDH standards.
Standards:
SONET is an American-based ANSI standard, while SDH is a European-based ETSI and ITU standard. Both are essentially the same and, therefore, often listed as SONET/SDH.
References
- Google DWDM search amazing
- Wavelength-division multiplexing Global Wiki
- ADVA used by BT customer premises equipment