Kubernetes/Networking
Pod networking
Networking in Kubernetes is using Linux Network namespace. Each Pod has IP address assosiated with it. It recives this IP from Virtual Ethernet interface pair.
Pod to pod communication on the same node. The pod cidr range was decided during cluster creation kubeadm init --pod-network=10.100.0.0/16 and notified CNI plugin (eg. Flannel, Calico) to use this IP range.
node-1
---pod1--- ---pod2---
|10.100.2.9| |10.100.2.7|
| eth0|----vethc3428d55 vethe10ac769----|eth0 |
---------- \ / ----------
bridge 10.100.2.1/24
|
eth0(node-1)172.31.11.11
---------|=====CNI overlay====|---------------------network--------------
eth0(node-2)172.31.22.22
| ---pod3---
| |10.100.1.5|
\------bridge-----------vetha1bbccdd----|eth0 |
----------
Find out node that 'nginx' pod is running on
kubectl -n default get pods -owide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-7cdbd8cdc9-89zcf 1/1 Running 1 8d 10.100.2.9 worker-2.acme.com <none> <none>
Ssh to worker-2.acme.com
user@worker-2:~$ ifconfig
cni0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 86:5d:c7:93:72:d2
inet addr:10.100.2.1 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::845d:c7ff:fe93:72d2/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:29 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:64 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1900 (1.9 KB) TX bytes:7165 (7.1 KB)
docker0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 02:42:c7:1c:b8:23
inet addr:172.17.0.1 Bcast:172.17.255.255 Mask:255.255.0.0
UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 02:20:2e:90:a8:66
inet addr:172.31.122.65 Bcast:172.31.127.255 Mask:255.255.240.0
inet6 addr: 2a05:d018:85:e101:2177:162b:63d9:3600/128 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: fe80::20:2eff:fe90:a866/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:9001 Metric:1
RX packets:20293 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:15985 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:15733611 (15.7 MB) TX bytes:2550893 (2.5 MB)
flannel.1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr b2:3a:21:03:ec:13
inet addr:10.100.2.0 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.255.255
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:20 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:4741 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:4741 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1
RX bytes:543426 (543.4 KB) TX bytes:543426 (543.4 KB)
vethc3428d55 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 52:1e:12:8c:0d:34 #<- 6th interface
inet6 addr: fe80::501e:12ff:fe8c:d34/64 Scope:Link #its a pipe to the running pod
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:28 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:94 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:2264 (2.2 KB) TX bytes:10623 (10.6 KB)
vethe10ac769 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 56:b5:d4:48:33:cc
inet6 addr: fe80::54b5:d4ff:fe48:33cc/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:1 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:76 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:42 (42.0 B) TX bytes:9190 (9.1 KB)
See containers running on this node. The "/pause" container which pertains to nGinx container for the purpose of holding on to the pods network namespace.
sudo docker ps | grep nginx
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
1fc1244ca7d5 nginx "nginx -g" 44 minu Up 44 k8s_nginx_nginx-7cdbd8cdc9-89zcf_default_9c89e271-a07c-11e9-80e8-02f78428aaf6_2
367062cd2852 k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.1 "/pause" 44 minu Up 44 k8s_POD_nginx-7cdbd8cdc9-89zcf_default_9c89e271-a07c-11e9-80e8-02f78428aaf6_10
#See docker IP (has not worked)
docker inspect --format='{{range .NetworkSettings.Networks}}{{.IPAddress}}{{end}}' $INSTANCE_ID
#See the container PID
sudo docker inspect --format '{{ .State.Pid }}' 1fc1244ca7d5
5738
$ sudo nsenter -t 5738 -n ip addr #display the container networking
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: eth0@if6: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 8951 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 9e:3a:d3:66:46:bb brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.100.2.9/24 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
#eth0@if6: :- eth0 on a pod is linked to node's 6th interface
Service networking
Services allow our pods to move around, get deleted, and replicate, all without having to manually keep track of their IP addresses in the cluster. This is accomplished by creating one gateway to distribute packets evenly across all pods.
YAML for nginx NodePort service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-nodeport
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- nodePort: 30080 #port on each node on which this service is exposed when type=NodePort or LoadBalancer, by default auto-allocate
port: 80 #port that will be exposed by this service
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80 #port to access on the pods targeted by the service, by default same as 'port' above
#it's a port exposed by containers
selector:
app: nginx #service will be applied to each pod with this label
Service has been created on every node to listen on port 30080
sudo lsof -i6 | grep 30080 kube-prox 3202 root 9u IPv6 52872 0t0 TCP *:30080 (LISTEN)
Service and endpoint can be seem below
kubectl get service nginx -owide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR nginx NodePort 10.110.225.169 <none> 80:30080/TCP 9d run=nginx kubectl get endpoints -owide NAME ENDPOINTS AGE kubernetes 172.31.115.255:6443 11d nginx 10.100.2.11:80 9d
iptables associated with the service above can be seen below
sudo iptables-save | grep KUBE | grep nginx -A KUBE-NODEPORTS -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx:" -m tcp --dport 30080 -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ -A KUBE-NODEPORTS -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx:" -m tcp --dport 30080 -j KUBE-SVC-4N57TFCL4MD7ZTDA -A KUBE-SERVICES ! -s 10.100.0.0/16 -d 10.110.225.169/32 -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx: cluster IP" -m tcp --dport 80 -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ #anything from -source (pod cidr 10.100.0.0/16, this will come from nginx service endpoint 10.100.2.11:80) #-destined to the service (nginx NodePort ip 10.110.225.169) redirect with a random pod associated with this service -A KUBE-SERVICES -d 10.110.225.169/32 -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx: cluster IP" -m tcp --dport 80 -j KUBE-SVC-4N57TFCL4MD7ZTDA
LoadBalancer networking
Loadbalancer is an extension of NodePort type of service. Loadbalancer redirect traffic to all nodes and NodePort. LoadBalancers are not pod aware, as nodes are its backend. The traffic to the right pod is controlled by IPtables. See below. If request from LoadBalancer is sent to Node-3, to reach a pod:80. There is no pod serving port 80 on Node-3. Therefore IPTables will route traffic to another node here: Node-1 or 2 (this is overlay network). Then the reply, will be routed back to Node-3 and out through LoadBalancer. This all means extra hops and latency.
.
LoadBalancer
IP: 22.111.222.33
/ | \
Node-1 Node-2 Node-3
172.10.10.11 172.10.11.22 172.10.12.33
NodePort:33623 NodePort:33623 NodePort:33623
Service:8080:80 Service:8080:80 Service:8080:80
pod1 10.100.1.1:80 pod4 10.100.2.1:80 pod6 10.100.3.1:81
pod2 10.100.1.2:81 pod5 10.100.2.2:81
pod3 10.100.1.3:82
LoadBalancer YAML spec. NodePort is not specifed as K8s will assign one and will manage it.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-loadbalancer
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
Create a loadbalancer by exposing a deployment
<souce lang=bash>
kubectl run nginx-loadbalancer --image=nginx
kubectl scale deployment/nginx-loadbalancer --replicas=2
kubectl expose deployment nginx-loadbalancer --port 80 --target-port 8080 --type LoadBalancer
</source>
Influence traffic flow
<souce lang=bash>
kubectl describe service nginx-loadbalancer
Name: nginx-loadbalancer
Namespace: default
Labels: run=nginx-loadbalancer
Annotations: <none> #annotated -> ExternalTrafficPolicy: Local
Selector: run=nginx-loadbalancer
Type: LoadBalancer
IP: 10.97.188.223
Port: <unset> 80/TCP
TargetPort: 8080/TCP
NodePort: <unset> 31154/TCP
Endpoints: 10.100.1.10:8080
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events: <none>
- Add addnotation, so traffic is routed to a pod on a local node if exists.
kubectl annotate service nginx-loadbalancer ExternalTrafficPolicy=Local </source>
Ingress networking
Ingress YAML spec
cat > ingress.yml <<EOF
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: service-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: acme.example.com #must be valid domain
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: nginx-1
servicePort: 80
- host: app.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: nginx-2
servicePort: 80
- http: #any traffic not matching HEADER: <hostnames> above
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: httpd-3
servicePort: 80
EOF
Resource can be managed like any other K8s resources
kubectl apply -f ingress kubectl edit ingress service-ingress
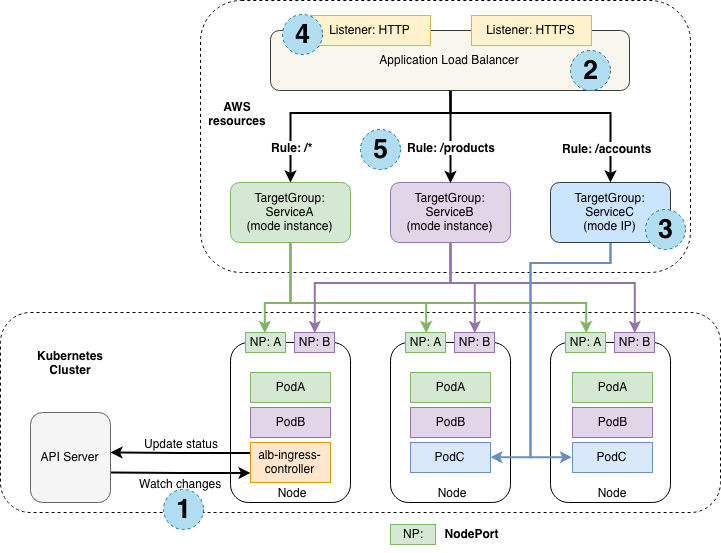
Summary diagram of AWS Kubernetes networking
References
- Service k8s docs