Difference between revisions of "Kubernetes/Istio"
| Line 343: | Line 343: | ||
# istio-1.7.3/samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml | # istio-1.7.3/samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml | ||
--- | --- | ||
# Entry point gateway | |||
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 | apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 | ||
kind: Gateway | kind: Gateway | ||
| Line 358: | Line 359: | ||
- "*" | - "*" | ||
--- | --- | ||
# Routes traffic to destination, could use subset for Traffic Shifting | |||
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 | apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 | ||
kind: VirtualService | kind: VirtualService | ||
| Line 384: | Line 386: | ||
port: | port: | ||
number: 9080 | number: 9080 | ||
#subset: v1 # [1] if defined in DestinationRule for the host ('productpage'), it will route to any pods | |||
# matching a label(s) defined in the subset | |||
# samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml | # samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml | ||
| Line 392: | Line 396: | ||
spec: | spec: | ||
host: productpage | host: productpage | ||
subsets: # pod selectors matching labels | subsets: # pod selectors matching labels | ||
- name: v1 | - name: v1 # [1] subset name for the host 'productpage' | ||
labels: | labels: | ||
version: v1 | version: v1 | ||
Revision as of 00:42, 25 October 2020
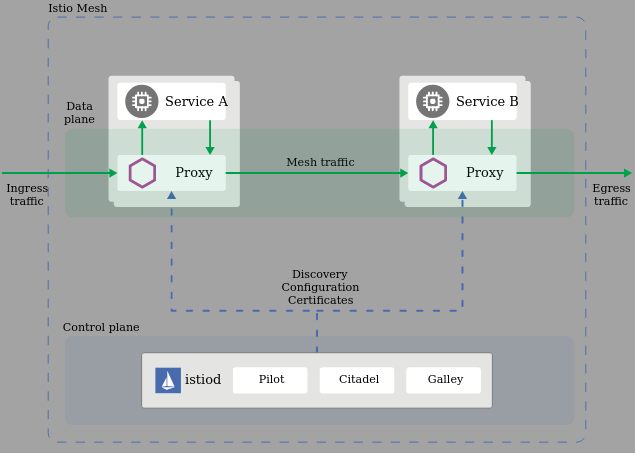
Architecture Istio v1.7
Namespace: <app namespace> | app1 | | app2 | # main container | proxy | <----------> | proxy | # Data Plane (all Envoy sidecar proxies) | pod | | pod | Namespace: istio-system | |citadel| |mixer| |pilot| | | | pod | | pod | | pod | | | C o n t r o l P l a n e A P I | ----------------------------------------
Note: All proxies are collectively named Data Plane and everything else that Istio deployed is called Control Plane
Note: Proxy term meaning is when someone has authority to represent someone. In software proxy components are invisible to clients. proxies
Istio components
- Istio-telemetry
- Istio-pilot
- Istio-tracing
| Envoy L7 proxy | Pilot | Citadel | Mixer[deprecate] | Galley |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Converts Istio configuration into a format that Envoy can understand. Aware about pods health, what pods are available and sends to the proxy pods that are alive with any other configuration updates.
|
Manages certificates, allows to enable TLS/SSL across entire cluster.
Pods
It's certificate store. |
It has a lot of modules/plugins. Pods: istio-policy-* istio-telemetry-* |
Interface for underlying Istio API gateway(aka server). It reads in k8s yaml and transforms it into internal structure Istio understand. |
Istio UI components:
- grafana:3000 - dashboards
- kiali:31000 - visualisation, tells what services are part of istio, how are they connected and performing
- jaeger:31001 - tracing
- Noticeable changes
- In Istio 1.6, completed transition and fully moved functionality into Istiod. This has allow to remove the separate deployments for Citadel, the sidecar injector, and Galley.
Istio on minikube
# Minimum requirements are 8G and 4 CPUs PROFILE=minikube-v1.17.6-istio minikube start --memory=8192 --cpus=4 --kubernetes-version=v1.17.6 --profile $PROFILE minikube start --memory=8192 --cpus=4 --kubernetes-version=v1.17.6 --driver kvm --profile $PROFILE-kvm2 minikube tunnel --profile $PROFILE minikube addons enable istio --profile $PROFILE # [1] error
Troubleshooting
- [1] - no matches for kind "IstioOperator"
💣 enable failed: run callbacks: running callbacks: [sudo KUBECONFIG=/var/lib/minikube/kubeconfig /var/lib/minikube/binaries/v1.17.6/kubectl apply -f /etc/kubernetes/addons/istio-default-profile.yaml: Process exited with status 1 stdout: namespace/istio-system unchanged stderr: error: unable to recognize "/etc/kubernetes/addons/istio-default-profile.yaml": no matches for kind "IstioOperator" in version "install.istio.io/v1alpha1"
Install istioctl tool
# Istio 1.6.x - option-1 curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=1.6.8 sh - cd istio-1.6.8/ # istio package directory export PATH=$PWD/bin:$PATH export PATH=$PATH:/git3rd/istio-1.6.8/bin # Istio 1.7.x - option-2 export ISTIO_VERSION=1.7.3 curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh - export PATH=$PWD/istio-$ISTIO_VERSION/bin:$PATH export ISTIO_INSTALL_DIR=$PWD/istio-$ISTIO_VERSION # Check version istioctl version --remote client version: 1.7.3 control plane version: 1.7.3 data plane version: 1.7.3 (7 proxies) # make sure you can connect to k8s cluster, then verify the install istioctl verify-install ... CustomResourceDefinition: templates.config.istio.io.default checked successfully CustomResourceDefinition: istiooperators.install.istio.io.default checked successfully Checked 25 custom resource definitions Checked 1 Istio Deployments Istio is installed successfully # Verify mesh coverage and config status istioctl proxy-status NAME CDS LDS EDS RDS ISTIOD VERSION details-v1-5974b67c8-xbp8l.default SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED istiod-5c6b7b5b8f-9npdz 1.7.3 istio-ingressgateway-5689f7c67-gvrh8.istio-system SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED istiod-5c6b7b5b8f-9npdz 1.7.3 ...
Install the control plane
Istio maintainers with increasing complexity of the project that goes against the user friendliness still support helm manifest based configuration although there is fair movement towards the operator pattern. See below for differences, v1.6 and v1.7 still support both methods.
# Tested with 1.7.3 istioctl install --skip-confirmation --set profile=default --dry-run # via operator istioctl manifest install --skip-confirmation --set profile=default --dry-run # via helm chart # Uses istio operator, the install can be replaced with 'upgrade' istioctl install --skip-confirmation --set profile=default \ --set kiali.enabled=true \ --set prometheus.enabled=true \ --dry-run # Using helm templates, notice the prefix 'values.' istioctl manifest install --skip-confirmation --set profile=default \ --set values.kiali.enabled=true \ --set values.prometheus.enabled=true \ --dry-run
Uninstall Istio
Uninstall v1.6.8, it's safe to ignore RBAC not existing resources.
istioctl manifest generate --set profile=default | kubectl delete --ignore-not-found=true -f - kubectl delete namespace istio-system
istioctl x uninstall --purge
Get info
Profiles are istiooperators.install.istio.io CRD manifests located in istio-1.7.3/manifests/profiles
# List profiles istioctl profile list ls istio-1.7.3/manifests/profiles default.yaml demo.yaml empty.yaml minimal.yaml preview.yaml remote.yaml # profile configuration istioctl profile dump demo istioctl profile dump --config-path components.pilot demo # Differences in the profiles istioctl profile diff default demo
Istio operator (v1.7.3), this is not super clear to me
find . -iname *operator*
./samples/operator
./samples/addons/extras/prometheus-operator.yaml
./manifests/charts/istio-operator # it's a chart to deploy operator
./manifests/charts/istio-operator/crds/crd-operator.yaml
./manifests/charts/base/crds/crd-operator.yaml
./manifests/charts/istio-telemetry/prometheusOperator
./manifests/deploy/crds/istio_v1alpha1_istiooperator_crd.yaml
./manifests/deploy/crds/istio_v1alpha1_istiooperator_cr.yaml
./manifests/deploy/operator.yaml # this [1]
./manifests/examples/customresource/istio_v1alpha1_istiooperator_cr.yaml
# [1] manifests/deploy/operator.yaml
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
namespace: istio-operator
name: istio-operator
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: istio-operator
...
# This API get always installed
k -n istio-system get istiooperators.install.istio.io # kind: IstioOperator
# List all Istio CRDs
k get crd -A | grep istio | cut -f1 -d" "
adapters.config.istio.io
attributemanifests.config.istio.io
authorizationpolicies.security.istio.io
destinationrules.networking.istio.io
envoyfilters.networking.istio.io
gateways.networking.istio.io
handlers.config.istio.io
httpapispecbindings.config.istio.io
httpapispecs.config.istio.io
instances.config.istio.io
istiooperators.install.istio.io
peerauthentications.security.istio.io
quotaspecbindings.config.istio.io
quotaspecs.config.istio.io
requestauthentications.security.istio.io
rules.config.istio.io
serviceentries.networking.istio.io
sidecars.networking.istio.io
templates.config.istio.io
virtualservices.networking.istio.io
workloadentries.networking.istio.io
CRDs aka new kind: objects - demystified
- Envoy terminiology Host, Downstream, Upstream, Listener, Cluster, Mesh, Runtime configuration
- Cluster: A cluster is a group of logically similar upstream hosts that Envoy connects to, eg. group of pods
reviewsservice v1, v2 and v3. - Cluster Discovery Service (CDS)
- Listener discovery service (LDS)
- Endpoint discovery service (EDS); cluster members are called endpoint.
- Route Discovery Service (RDS)
- Cluster: A cluster is a group of logically similar upstream hosts that Envoy connects to, eg. group of pods
VirtualServicesandDestinationRulesare key resources for configuring Istio’s traffic routing functionality.VirtualServices- is used to configure how requests are routed to a service within an Istio service mesh, define how traffic is routed to a given destinationDestinationRulesdefine policies that apply to traffic intended for a service after routing has occurred. ADestinationRulesis applied afterVirtualServicesrouting rules are evaluated, so they apply to the traffic’s real destination.subsets- defines a set of pods with common matching label eg.version: v1
gateways- taps on to ingressgateway; describe which controller to use eg. plugs into real network received byservice/istio-ingressgatewaythat has labelistio=ingressgatewayvirtualservices- it bounds to a gateway(s), and describes how requests are routed to a service within the meshdestinationrules- applied aftervsrouting rules to real traffic destination, defines available versions called subsets
adaptersattributemanifestsauthorizationpoliciesenvoyfiltershandlershttpapispecbindingshttpapispecsinstancesistiooperatorspeerauthenticationsquotaspecbindingsquotaspecsrequestauthenticationsrulesserviceentriessidecarstemplatesworkloadentries
Customize istio installation
Configure ingress-gateways
Gateways are a special type of component, since multiple ingress and egress gateways can be defined. In the IstioOperator API, gateways are defined as a list type. The default profile installs one ingress gateway, called istio-ingressgateway.
# Show default values of the ingressgateway istioctl profile dump --config-path components.ingressGateways istioctl profile dump --config-path values.gateways.istio-ingressgateway
Install istio with ingressgateway servioce as internal AWS loadbalancer:
istioctl install \ --set profile=default \ --set addonComponents.prometheus.enabled=false \ --set addonComponents.grafana.enabled=false \ --set addonComponents.kiali.enabled=false \ --set addonComponents.tracing.enabled=false \ --set components.ingressGateways[0].enabled="true" \ --set components.ingressGateways[0].k8s.serviceAnnotations."service\.beta\.kubernetes\.io/aws-load-balancer-internal"=\"true\" ✔ Istio core installed ✔ Istiod installed ✔ Ingress gateways installed ✔ Installation complete # --set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.serviceAnnotations."service\.beta\.kubernetes\.io/aws-load-balancer-internal"="0\.0\.0\.0/0" istioctl version --remote client version: 1.6.4 control plane version: 1.6.4 data plane version: 1.6.4 (1 proxies)
Ingress Gateways - controller
# manually inject the sidecar
kubectl -n bin apply -f <(istioctl kube-inject -f httpbin.yaml)
export INGRESS_HOST=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
# AWS, uses 'hostname'
export INGRESS_HOST=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}')
export INGRESS_PORT=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].port}')
export SECURE_INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="https")].port}')
# This is not necessary set/configured
export TCP_INGRESS_PORT=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="tcp")].port}')
# Verify
env | grep INGRESS
Bookinfo examples - gateway, virtualservice
# istio-1.7.3/samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
---
# Entry point gateway
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway # use istio default controller
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
# Routes traffic to destination, could use subset for Traffic Shifting
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: bookinfo
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- bookinfo-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /productpage
- uri:
prefix: /static
- uri:
exact: /login
- uri:
exact: /logout
- uri:
prefix: /api/v1/products
route:
- destination:
host: productpage
port:
number: 9080
#subset: v1 # [1] if defined in DestinationRule for the host ('productpage'), it will route to any pods
# matching a label(s) defined in the subset
# samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: productpage
spec:
host: productpage
subsets: # pod selectors matching labels
- name: v1 # [1] subset name for the host 'productpage'
labels:
version: v1
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: reviews
spec:
host: reviews
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
- name: v3
labels:
version: v3
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: ratings
spec:
host: ratings
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
- name: v2-mysql
labels:
version: v2-mysql
- name: v2-mysql-vm
labels:
version: v2-mysql-vm
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: details
spec:
host: details
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
---
Kiali visualisations
You install kiali manually from scratch or pass arg to istioctl
# Create user name and password
KIALI_USERNAME=admin
KIALI_PASSPHRASE=admin
kubectl apply -f <(cat <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kiali
namespace: istio-system
labels:
app: kiali
stringData:
username: $KIALI_USERNAME
passphrase: $KIALI_PASSPHRASE
EOF
)
istioctl manifest install \
--set values.kiali.enabled=true \
--set values.prometheus.enabled=true
kubectl wait --for=condition=Available deployment/kiali -n istio-system --timeout=300s
# Access the dashboard
istioctl dashboard kiali
Add custom headers
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: httpbin
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- httpbin-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /headers
route:
- destination:
port:
number: 8000
host: httpbin
headers:
response: # add to response
add:
"key1": "abc"
request: # add to request
add:
"key2": "def"
Resources
- gitops-istio Istio on a Kubernetes cluster and automating A/B testing and canary releases with GitOps pipelines example
Training Istio v1.5
- What is Istio Service Mesh?
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 1
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 2 - Enabling Sidecar Injection
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 3 - Visualizing the System with Kiali
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 4 - Finding Performance Problems
- istio-fleetman Github source materials
- Istio Architecture Part 1 - Proxies
- Istio Architecture Part 2 - The Data Plane and Envoy
- Istio Architecture Part 3 - The Control Plane
- Istio Architecture Part 4 - Going Deeper into Envoy
Istio v1.7
- VM <-> K8s mesh demo at 30 min