Difference between revisions of "Kubernetes/Networking"
(→Proxy) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= ClusterIP = | |||
<code>ClusterIP</code> is the IP for the K8s service which is nothing but a magic of "IP Tables Rules". Kube-Proxy is responsible to write ip table rules in every node once you define <code>Service</code>. These ip table rules or ClusterIP points to actual pod IP(The IP assigned by flannel daemon). | |||
= Pod networking = | = Pod networking = | ||
Networking in Kubernetes is using Linux Network namespace. Each Pod has IP address assosiated with it. It recives this IP from Virtual Ethernet interface pair. | Networking in Kubernetes is using Linux Network namespace. Each Pod has IP address assosiated with it. It recives this IP from Virtual Ethernet interface pair. | ||
| Line 119: | Line 122: | ||
#eth0@if6: :- eth0 on a pod is linked to node's 6th interface | #eth0@if6: :- eth0 on a pod is linked to node's 6th interface | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
= Service networking = | = Service networking = | ||
Services allow our pods to move around, get deleted, and replicate, all without having to manually keep track of their IP addresses in the cluster. This is accomplished by creating one gateway to distribute packets evenly across all pods. | Services allow our pods to move around, get deleted, and replicate, all without having to manually keep track of their IP addresses in the cluster. This is accomplished by creating one gateway to distribute packets evenly across all pods. | ||
Revision as of 22:37, 27 September 2019
ClusterIP
ClusterIP is the IP for the K8s service which is nothing but a magic of "IP Tables Rules". Kube-Proxy is responsible to write ip table rules in every node once you define Service. These ip table rules or ClusterIP points to actual pod IP(The IP assigned by flannel daemon).
Pod networking
Networking in Kubernetes is using Linux Network namespace. Each Pod has IP address assosiated with it. It recives this IP from Virtual Ethernet interface pair.
Pod to pod communication on the same node. The pod cidr range was decided during cluster creation kubeadm init --pod-network=10.100.0.0/16 and notified CNI plugin (eg. Flannel, Calico) to use this IP range.
node-1
---pod1--- ---pod2---
|10.100.2.9| |10.100.2.7|
| eth0|----vethc3428d55 vethe10ac769----|eth0 |
---------- \ / ----------
bridge 10.100.2.1/24
|
eth0(node-1)172.31.11.11
---------|=====CNI overlay====|---------------------network--------------
eth0(node-2)172.31.22.22
| ---pod3---
| |10.100.1.5|
\------bridge-----------vetha1bbccdd----|eth0 |
----------
Find out node that 'nginx' pod is running on
kubectl -n default get pods -owide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-7cdbd8cdc9-89zcf 1/1 Running 1 8d 10.100.2.9 worker-2.acme.com <none> <none>
Ssh to worker-2.acme.com
user@worker-2:~$ ifconfig
cni0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 86:5d:c7:93:72:d2
inet addr:10.100.2.1 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::845d:c7ff:fe93:72d2/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:29 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:64 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1900 (1.9 KB) TX bytes:7165 (7.1 KB)
docker0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 02:42:c7:1c:b8:23
inet addr:172.17.0.1 Bcast:172.17.255.255 Mask:255.255.0.0
UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 02:20:2e:90:a8:66
inet addr:172.31.122.65 Bcast:172.31.127.255 Mask:255.255.240.0
inet6 addr: 2a05:d018:85:e101:2177:162b:63d9:3600/128 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: fe80::20:2eff:fe90:a866/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:9001 Metric:1
RX packets:20293 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:15985 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:15733611 (15.7 MB) TX bytes:2550893 (2.5 MB)
flannel.1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr b2:3a:21:03:ec:13
inet addr:10.100.2.0 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.255.255
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:20 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:4741 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:4741 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1
RX bytes:543426 (543.4 KB) TX bytes:543426 (543.4 KB)
vethc3428d55 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 52:1e:12:8c:0d:34 #<- 6th interface
inet6 addr: fe80::501e:12ff:fe8c:d34/64 Scope:Link #its a pipe to the running pod
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:28 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:94 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:2264 (2.2 KB) TX bytes:10623 (10.6 KB)
vethe10ac769 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 56:b5:d4:48:33:cc
inet6 addr: fe80::54b5:d4ff:fe48:33cc/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:8951 Metric:1
RX packets:1 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:76 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:42 (42.0 B) TX bytes:9190 (9.1 KB)
See containers running on this node. The "/pause" container which pertains to nGinx container for the purpose of holding on to the pods network namespace.
sudo docker ps | grep nginx
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
1fc1244ca7d5 nginx "nginx -g" 44 minu Up 44 k8s_nginx_nginx-7cdbd8cdc9-89zcf_default_9c89e271-a07c-11e9-80e8-02f78428aaf6_2
367062cd2852 k8s.gcr.io/pause:3.1 "/pause" 44 minu Up 44 k8s_POD_nginx-7cdbd8cdc9-89zcf_default_9c89e271-a07c-11e9-80e8-02f78428aaf6_10
#See docker IP (has not worked)
docker inspect --format='{{range .NetworkSettings.Networks}}{{.IPAddress}}{{end}}' $INSTANCE_ID
#See the container PID
sudo docker inspect --format '{{ .State.Pid }}' 1fc1244ca7d5
5738
$ sudo nsenter -t 5738 -n ip addr #display the container networking
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: eth0@if6: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 8951 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 9e:3a:d3:66:46:bb brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 10.100.2.9/24 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
#eth0@if6: :- eth0 on a pod is linked to node's 6th interface
Service networking
Services allow our pods to move around, get deleted, and replicate, all without having to manually keep track of their IP addresses in the cluster. This is accomplished by creating one gateway to distribute packets evenly across all pods.
YAML for nginx NodePort service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-nodeport
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- nodePort: 30080 #port on each node on which this service is exposed when type=NodePort or LoadBalancer, by default auto-allocate
port: 80 #port that will be exposed by this service
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80 #port to access on the pods targeted by the service, by default same as 'port' above
#it's a port exposed by containers
selector:
app: nginx #service will be applied to each pod with this label
Service has been created on every node to listen on port 30080
sudo lsof -i6 | grep 30080 kube-prox 3202 root 9u IPv6 52872 0t0 TCP *:30080 (LISTEN)
Service and endpoint can be seem below
kubectl get service nginx -owide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR nginx NodePort 10.110.225.169 <none> 80:30080/TCP 9d run=nginx kubectl get endpoints -owide NAME ENDPOINTS AGE kubernetes 172.31.115.255:6443 11d nginx 10.100.2.11:80 9d # Another example, showing an application 'rediness-app' is having 3 pods behind its service $ kubectl get endpoints NAME ENDPOINTS AGE kubernetes 35.205.145.199:443 26d readiness-app 10.60.0.23:8080,10.60.1.9:8080,10.60.2.24:8080 7m6s
iptables associated with the service above can be seen below
sudo iptables-save | grep KUBE | grep nginx -A KUBE-NODEPORTS -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx:" -m tcp --dport 30080 -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ -A KUBE-NODEPORTS -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx:" -m tcp --dport 30080 -j KUBE-SVC-4N57TFCL4MD7ZTDA -A KUBE-SERVICES ! -s 10.100.0.0/16 -d 10.110.225.169/32 -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx: cluster IP" -m tcp --dport 80 -j KUBE-MARK-MASQ #anything from -source (pod cidr 10.100.0.0/16, this will come from nginx service endpoint 10.100.2.11:80) #-destined to the service (nginx NodePort ip 10.110.225.169) redirect with a random pod associated with this service -A KUBE-SERVICES -d 10.110.225.169/32 -p tcp -m comment --comment "default/nginx: cluster IP" -m tcp --dport 80 -j KUBE-SVC-4N57TFCL4MD7ZTDA
Port-forward
Forward one or more local ports to a pod. This command requires the node to have socat installed. You can port-forward traffic only to a pod selected by service or deployment. This feature is only used for debugging. Examples:
# Listen on ports 5000 and 6000 locally, forwarding data to/from ports 5000 and 6000 in the pod /or # pods selected by a service or deployment kubectl port-forward pod/mypod 5000 6000 # forwarding to the pod kubectl port-forward service/myservice 5000 6000 # forwarding to a selected (rnd) pod by the service kubectl port-forward deployment/mydeployment 5000 6000 # forwarding to a selected (rnd) pod by the deployment # Listen on port 8888 locally, forwarding to 5000 in the pod kubectl port-forward pod/mypod 8888:5000 kubectl port-forward service/kibana --address=0.0.0.0 8888:5000 # listen on all IPs
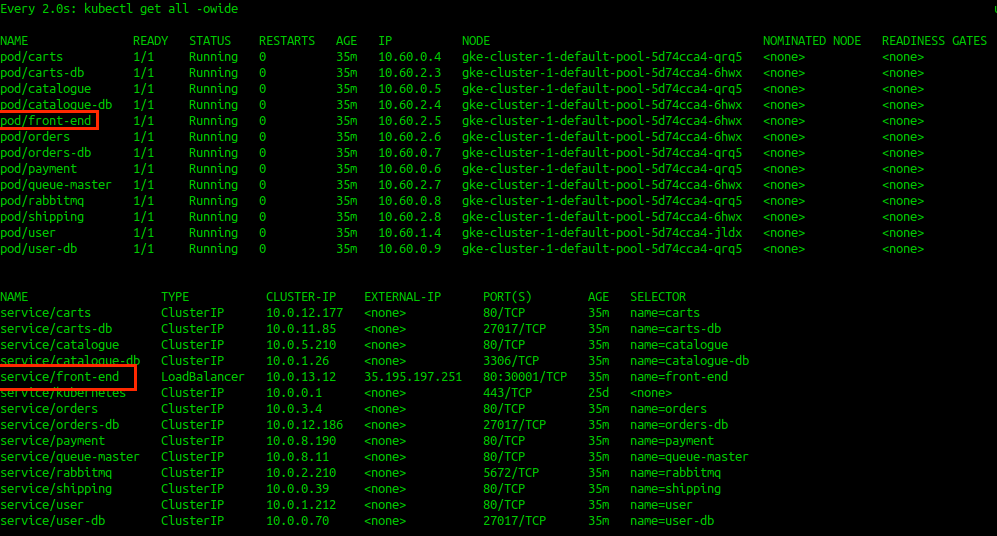
This is a status of deployed applications, note frond-end application, we are trying to access localy
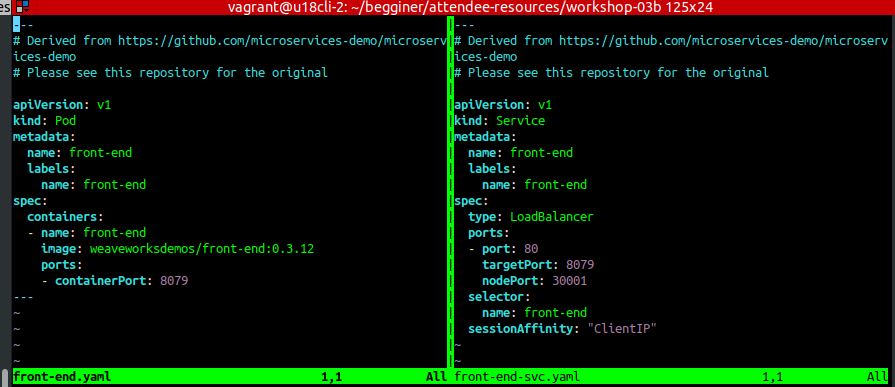
We can port-forward remote kubernetes service port to local machine. Let's assume we have config like this:
Create port-forwarding, your host will start listening on port TCP:8079. If your pod is exposing port below <1024 you should then you need to specify local port to target pod, then use eg: 8089:80. First port is local port, second is the container port.
$ kubectl port-forward front-end 8079 Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8079 -> 8079 Forwarding from [::1]:8079 -> 8079 Handling connection for 8079 #In a new terminal try to reach to the frond-end curl http://localhost:8079
Proxy
Creates a proxy server or application-level gateway between localhost and the Kubernetes API Server. It also allows serving static content over specified HTTP path. All incoming data enters through one port and gets forwarded to the remote kubernetes API Server port, except for the path matching the static content path.
# Proxy all of the kubernetes api and nothing else kubectl proxy --api-prefix=/
Ssh to node
gcloud compute ssh gke-cluster-1-default-pool-5d74cca4-6hwx $ gcloud compute ssh gke-cluster-1-default-pool-5d74cca4-6hwx WARNING: The public SSH key file for gcloud does not exist. WARNING: The private SSH key file for gcloud does not exist. WARNING: You do not have an SSH key for gcloud. WARNING: SSH keygen will be executed to generate a key. Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/vagrant/.ssh/google_compute_engine. Your public key has been saved in /home/vagrant/.ssh/google_compute_engine.pub. The key fingerprint is: SHA256:V8S2tzis6NPGfFdKzUak0IX0aRUBin3jW+wCMFqfoYA vagrant@u18cli-2 The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 2048]----+ | ..+o==| | . o.= o.+| | E . = =.= =.| | + =.* * .| | .S..= + B | | . = * =| | = . = = | | o * . + | | ..o . . | +----[SHA256]-----+ Updating project ssh metadata...⠹Updated [https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/responsive-sun-246311]. Updating project ssh metadata...done. Waiting for SSH key to propagate. Warning: Permanently added 'compute.7391123279603721012' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. ############################################################################## # WARNING: Any changes on the boot disk of the node must be made via # DaemonSet in order to preserve them across node (re)creations. # Node will be (re)created during manual-upgrade, auto-upgrade, # auto-repair or auto-scaling. # See https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/concepts/node-images#modifications # for more information. ############################################################################## ############################################################################## # WARNING: Any changes on the boot disk of the node must be made via # DaemonSet in order to preserve them across node (re)creations. # Node will be (re)created during manual-upgrade, auto-upgrade, # auto-repair or auto-scaling. # See https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/concepts/node-images#modifications # for more information. ############################################################################## Welcome to Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.15.0-1034-gke x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage This system has been minimized by removing packages and content that are not required on a system that users do not log into. To restore this content, you can run the 'unminimize' command. 0 packages can be updated. 0 updates are security updates. Welcome to Kubernetes v1.13.7-gke.8! You can find documentation for Kubernetes at: http://docs.kubernetes.io/ The source for this release can be found at: /home/kubernetes/kubernetes-src.tar.gz Or you can download it at: https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release-gke/release/v1.13.7-gke.8/kubernetes-src.tar.gz It is based on the Kubernetes source at: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/v1.13.7-gke.8 For Kubernetes copyright and licensing information, see: /home/kubernetes/LICENSES
LoadBalancer networking
Loadbalancer is an extension of NodePort type of service. Loadbalancer redirect traffic to all nodes and NodePort. LoadBalancers are not pod aware, as nodes are its backend. The traffic to the right pod is controlled by IPtables. See below. If request from LoadBalancer is sent to Node-3, to reach a pod:80. There is no pod serving port 80 on Node-3. Therefore IPTables will route traffic to another node here: Node-1 or 2 (this is overlay network). Then the reply, will be routed back to Node-3 and out through LoadBalancer. This all means extra hops and latency.
.
LoadBalancer
IP: 22.111.222.33
/ | \
Node-1 Node-2 Node-3
172.10.10.11 172.10.11.22 172.10.12.33
NodePort:33623 NodePort:33623 NodePort:33623
Service:8080:80 Service:8080:80 Service:8080:80
pod1 10.100.1.1:80 pod4 10.100.2.1:80 pod6 10.100.3.1:81
pod2 10.100.1.2:81 pod5 10.100.2.2:81
pod3 10.100.1.3:82
LoadBalancer YAML spec. NodePort is not specifed as K8s will assign one and will manage it.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-loadbalancer
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
Create a loadbalancer by exposing a deployment
<souce lang=bash>
kubectl run nginx-loadbalancer --image=nginx
kubectl scale deployment/nginx-loadbalancer --replicas=2
kubectl expose deployment nginx-loadbalancer --port 80 --target-port 8080 --type LoadBalancer
</source>
Influence traffic flow
<souce lang=bash>
kubectl describe service nginx-loadbalancer
Name: nginx-loadbalancer
Namespace: default
Labels: run=nginx-loadbalancer
Annotations: <none> #annotated -> ExternalTrafficPolicy: Local
Selector: run=nginx-loadbalancer
Type: LoadBalancer
IP: 10.97.188.223
Port: <unset> 80/TCP
TargetPort: 8080/TCP
NodePort: <unset> 31154/TCP
Endpoints: 10.100.1.10:8080
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events: <none>
- Add addnotation, so traffic is routed to a pod on a local node if exists.
kubectl annotate service nginx-loadbalancer ExternalTrafficPolicy=Local </source>
Ingress networking
Ingress YAML spec
cat > ingress.yml <<EOF
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: service-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: acme.example.com #must be valid domain
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: nginx-1
servicePort: 80
- host: app.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: nginx-2
servicePort: 80
- http: #any traffic not matching HEADER: <hostnames> above
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: httpd-3
servicePort: 80
EOF
Resource can be managed like any other K8s resources
kubectl apply -f ingress kubectl edit ingress service-ingress
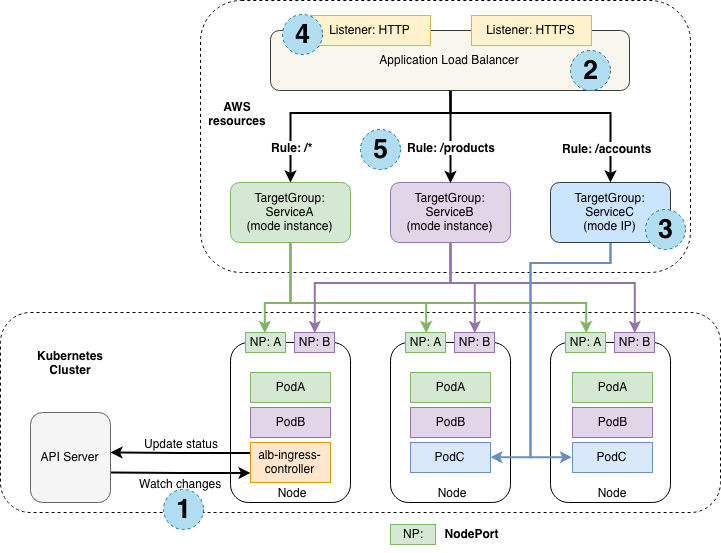
Summary diagram of AWS Kubernetes networking
DNS
Since 1.13, CoreOS has replaced kube-dns with core-dns written in Go. It supports DNS over TLS in short dot. core-dns pods are running as a deployment.
#svc-name ns /BaseDomainName\ kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local 10-10-20-1.default.pod.cluster.local #pod ip ns \BaseDomainName/
Core-dns runs as a deployment
kubectl -n kube-system get pod -owide | grep core coredns-86c58d9df4-7dl5d 1/1 Running 59 12d 10.100.0.18 master-1.acme.com <none> <none> coredns-86c58d9df4-rsxct 1/1 Running 59 12d 10.100.0.19 master-1.acme.com <none> <none> kubectl -n kube-system get deployments -owide NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR coredns 2/2 2 2 12d coredns k8s.gcr.io/coredns:1.2.6 k8s-app=kube-dns #Service that perform LoadBalancing. note it's named 'kube-dns' to support backward compatibnility for workloads relaying on kube-dns ubectl -n kube-system get service -owide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP 12d k8s-app=kube-dns
Interact with DNS, using BusyBox container
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: busybox
namespace: default
spec:
containers:
- image: busybox:1.28.4
command:
- sleep
- "3600"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: busybox
restartPolicy: Always
#Deploy
kubectl apply -f busybox.yaml
#Verify dns settings
kubectl exec -t busybox -- cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 10.96.0.10
search default.svc.cluster.local svc.cluster.local cluster.local mylabserver.com
options ndots:5
#Check DNS operations
kubectl exec -it busybox -- nslookup <service-name>
kubectl exec -it busybox -- nslookup <pod-ip-v-4>.default.pod.cluster.local #pod
kubectl exec -it busybox -- nslookup <svcName>.default.svc.cluster.local #service
kubectl exec -it busybox -- nslookup kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local #service
CoreDNS manages following records for Services:
- A records (not headless) - Services are assigned a DNS A record for a name of the form my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster-domain.example. This resolves to the cluster IP of the Service.
- A records (headless without cluster IP) - Services are also assigned a DNS A record for a name of the form my-svc.my-namespace.svc.cluster-domain.example. Unlike normal Services, this resolves to the set of IPs of the pods selected by the Service
- SRV records - SRV Records are created for named ports that are part of normal or Headless Services. read more...
Headless services, its a service without a clusterIP, will respond with set of IPs that belong to a POD. These IPs are current IPs that service consider healthy pods.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kube-headless
spec:
clusterIP: None #set to none
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: kubserve2
Custom dns settings can be set per pod basis. Default is cluster first, pod inherits DNS settings from a node it's running on
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-dns-custom-setup
spec:
containers:
- name: test
image: nginx
dnsPolicy: "None" #do not inherit settings from a node
dnsConfig:
nameservers:
- 8.8.4.4
searches:
- ns1.svc.cluster.local
- my.dns.search.suffix
options:
- name: ndots
value: "3"
- name: edns0
Troubleshot core-dns
kubectl -n kube-system get pods | grep dns coredns-86c58d9df4-7dl5d 1/1 Running 60 13d coredns-86c58d9df4-rsxct 1/1 Running 60 13d #See logs kubectl -n kube-system logs coredns-86c58d9df4-7dl5d -f .:53 2019-07-18T06:33:08.165Z [INFO] CoreDNS-1.2.6 2019-07-18T06:33:08.165Z [INFO] linux/amd64, go1.11.2, 756749c CoreDNS-1.2.6 linux/amd64, go1.11.2, 756749c [INFO] plugin/reload: Running configuration MD5 = f65c4821c8a9b7b5eb30fa4fbc167769 [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2 8726527267836830687.8090630885983783330. HINFO: unreachable backend: read udp 10.100.0.20:33021->172.31.0.2:53: i/o timeout
References
- Service
- Service k8s docs
- DNS