Difference between revisions of "Kubernetes/Istio"
| Line 347: | Line 347: | ||
ISTIO_META_DNS_CAPTURE: "true" | ISTIO_META_DNS_CAPTURE: "true" | ||
enablePrometheusMerge: true | enablePrometheusMerge: true | ||
discoverySelector: # new in v1.10, choose which namespaces Istiod should watch for configurations of services,endpoints,deployments | #discoverySelector: # new in v1.10, choose which namespaces Istiod should watch for configurations of services,endpoints,deployments | ||
- matchLabels: | #- matchLabels: | ||
# istio-discovery: enabled # <- example label | |||
# #env: prod | |||
# #region: us-east-1 | |||
- matchExpressions: | #- matchExpressions: | ||
# - key: app | |||
# operator: In | |||
# values: | |||
# - cassandrs | |||
# - spark | |||
EOF | EOF | ||
) --dry-run | ) --dry-run | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 31 May 2021
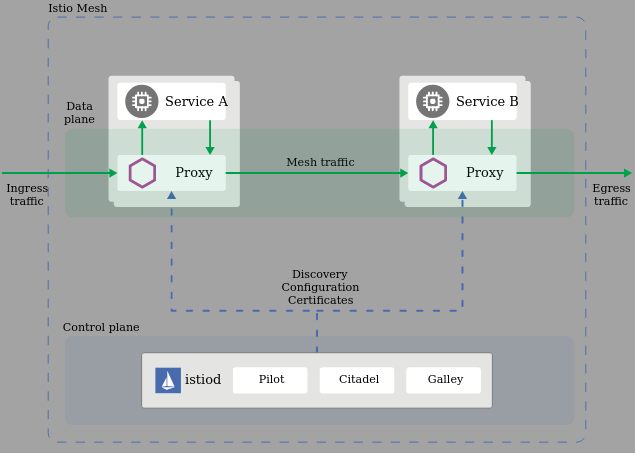
Architecture Istio ~v1.7+
Namespace: <app namespace> | app1 | | app2 | # main container | proxy | <----------> | proxy | # Data Plane (all Envoy sidecar proxies) | pod | | pod | Namespace: istio-system | |citadel| |mixer| |pilot| | | | pod | | pod | | pod | | | C o n t r o l P l a n e A P I | ----------------------------------------
Note: All proxies are collectively named Data Plane and everything else that Istio deployed is called Control Plane
Note: Proxy term meaning is when someone has authority to represent someone. In software proxy components are invisible to clients. proxies
Security Architecture
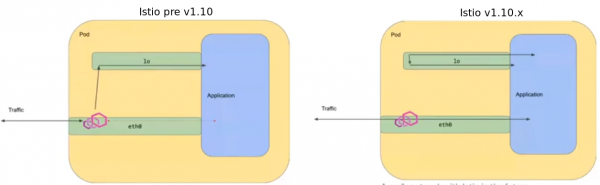
Pod networking changed v1.10 matching default Kubernetes behaviour
service/istiod: 15010 - grpc-xds 15012 - https-dns 15014 - http-monitoring 443 - https-webhook, container port 15017
Istio components
- Istio-telemetry
- Istio-pilot
- Istio-tracing
| Envoy L7 proxy | Pilot | Citadel | Mixer[deprecate] | Galley |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Converts Istio configuration into a format that Envoy can understand. Aware about pods health, what pods are available and sends to the proxy pods that are alive with any other configuration updates.
|
Manages certificates, allows to enable TLS/SSL across entire cluster.
Pods
It's certificate store. |
It has a lot of modules/plugins. Pods: istio-policy-* istio-telemetry-* |
Interface for underlying Istio API gateway(aka server). It reads in k8s yaml and transforms it into internal structure Istio understand. |
Istio UI components:
- grafana:3000 - dashboards
- kiali:31000 - visualisation, tells what services are part of istio, how are they connected and performing
- jaeger:31001 - tracing
- Noticeable changes
- In Istio 1.6, completed transition and fully moved functionality into Istiod. This has allow to remove the separate deployments for Citadel, the sidecar injector, and Galley.
Istio on minikube
# Minimum requirements are 8G and 4 CPUs K8SVERSION=v1.18.9 PROFILE=minikube-$K8SVERSION-istio minikube profile $PROFILE # set default profile minikube start --kubernetes-version=$K8SVERSION minikube start --memory=8192 --cpus=4 --kubernetes-version=$K8SVERSION --driver minikube minikube start --memory=8192 --cpus=4 --kubernetes-version=$K8SVERSION --driver kvm minikube tunnel minikube addons enable istio # [1] error
Troubleshooting
- [1] - no matches for kind "IstioOperator"
💣 enable failed: run callbacks: running callbacks: [sudo KUBECONFIG=/var/lib/minikube/kubeconfig /var/lib/minikube/binaries/v1.17.6/kubectl apply -f /etc/kubernetes/addons/istio-default-profile.yaml: Process exited with status 1 stdout: namespace/istio-system unchanged stderr: error: unable to recognize "/etc/kubernetes/addons/istio-default-profile.yaml": no matches for kind "IstioOperator" in version "install.istio.io/v1alpha1"
Install bookinfo example app.
Install
istioctl cli
The curl ISTIO_VERSION=1.10.0 sh - just downloads istio files into its own directory. It does not install anything
# Option_1 - the official approach curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=1.10.0 sh - cd istio-1.10.0/ # istio package directory export PATH=$PWD/bin:$PATH # Option_2 export ISTIO_VERSION=1.10.0 curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh - export PATH=$PWD/istio-$ISTIO_VERSION/bin:$PATH export ISTIO_INSTALL_DIR=$PWD/istio-$ISTIO_VERSION # Check version istioctl version --remote client version: 1.9.1 control plane version: 1.9.1 data plane version: 1.9.1 (7 proxies) # Pre-flight check istioctl x precheck # Verify the install istioctl verify-install ... CustomResourceDefinition: templates.config.istio.io.default checked successfully CustomResourceDefinition: istiooperators.install.istio.io.default checked successfully Checked 25 custom resource definitions Checked 1 Istio Deployments Istio is installed successfully # Verify mesh coverage and the config status istioctl proxy-status NAME CDS LDS EDS RDS ISTIOD VERSION details-v1-5974b67c8-xbp8l.default SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED istiod-5c6b7b5b8f-9npdz 1.9.1 istio-ingressgateway-5689f7c67-gvrh8.istio-system SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED istiod-5c6b7b5b8f-9npdz 1.9.1 ... # Analyse the mesh configuration istioctl analyze --all-namespaces
control plane
- Install with Istioctl - recommended
- Istio Operator Install
- Install with Helm
Istio maintainers with increasing complexity of the project that goes against the user friendliness still support helm manifest based configuration although there is fair movement towards the operator pattern. See below for differences, v1.6 and v1.7 still support both methods.
There are a few operational modes to configure control plane:
- istio operator
- install -
istioctl installwith--setor-f istio-overlay.yamlwill be overlayed on top of a chosen profile - reconfigure -
istioctl manifest apply -f istio-install.yaml --dry-run istio operator initinstalls the operator podistio-operator. Then usingkubectl apply -f istio-overlay.yamlwill trigger the operator to sync the changes. Also manually changingistio-system/istiooperators.install.istio.io/installed-stateobject will trigger an the operator event to sync the config and reconfigure teh control-plane.
- install -
- [deprecated]
istioctl manifest installwith--setor-f <manifests.yaml>
Install
# Tested with 1.7.3 [depreciating method via helm charts], --set values are prefixed with 'values.' istioctl manifest install --skip-confirmation --set profile=default \ --set values.kiali.enabled=true \ --set values.prometheus.enabled=true \ --dry-run # Tested with 1.8.2 [istio.operator via 'istioctl' cli] istioctl x precheck istioctl install --skip-confirmation --set profile=default --dry-run # via operator istioctl upgrade --skip-confirmation --set profile=default --dry-run # via operator
| Basic | +Kiali,Prometheus | +ServiceEntry, mesh traffic only | +egress |
|---|---|---|---|
| <syntaxhighlightjs lang=yaml>
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: profile: default EOF ) </syntaxhighlightjs> |
<syntaxhighlightjs lang=yaml>
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: profile: default
values:
kiali:
enabled: true
prometheus:
enabled: true
EOF ) </syntaxhighlightjs> |
<syntaxhighlightjs lang=yaml>
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: profile: default
values:
kiali:
enabled: true
# Kiali uses Prometheus to populate its dashboards
prometheus:
enabled: true
meshConfig:
# debugging
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
outboundTrafficPolicy:
mode: REGISTRY_ONLY
EOF ) </syntaxhighlightjs> |
<syntaxhighlightjs lang=yaml>
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: profile: default
components:
egressGateways:
- enabled: true
name: istio-egressgateway
values:
kiali:
enabled: true
prometheus:
enabled: true
meshConfig:
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
outboundTrafficPolicy:
mode: REGISTRY_ONLY
EOF ) </syntaxhighlightjs> |
- Uninstall
Uninstall v1.6.8, it's safe to ignore RBAC not existing resources.
istioctl manifest generate --set profile=default | kubectl delete --ignore-not-found=true -f - kubectl delete namespace istio-system
Uninstall v1.7.x - view logs
# Removes istio-system resources and istio-operator istioctl x uninstall --purge # cmd:experimental, aliases: experimental, x, exp ✔ Uninstall complete
Install - day 2 operation
This should be a preferred method for day 2 operations - canary upgrade where CP gets installed with revisions and Ingress-Gateway components are installed separately.
- Pre checks
istioctl experimental precheck istioctl analyze -A # Optional labels kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=disabled
- Install control-plane
Note: For installing v1.9.x you should first install without revisions eg.REVISION="" this is because revisions upgrade expects to have default revision set.
Note: Due to a bug in the creation of the ValidatingWebhookConfiguration during install, initial installations of Istio must not specify a revision. A workaround is to run command below, where <REVISION> is the name of the revision that should handle validation. This command creates an istiod service pointed to the target revision.
kubectl get service -n istio-system -o json istiod-<REVISION> | jq '.metadata.name = "istiod" | del(.spec.clusterIP) | del(.spec.clusterIPs)' | kubectl apply -f -
REVISION="" # don't use revisions
REVISION='--revision 1-10-0'
istioctl install -y -n istio-system $REVISION -f <(cat <<EOF
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
name: control-plane
#namespace: istio-system # it's default
spec:
profile: minimal # installs only control-plane
hub: gcr.io/istio-release
components:
pilot:
k8s:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 2
env:
- name: PILOT_FILTER_GATEWAY_CLUSTER_CONFIG # Reduce Gateway Config to services that have routing rules defined
value: "true"
meshConfig:
defaultConfig:
proxyMetadata:
# https://preliminary.istio.io/latest/blog/2020/dns-proxy/
# curl localhost:8080/debug/nsdz?proxyID=<POD-NAME>
# dig @localhost -p 15053 postgres-stolon-proxy.sample.svc
ISTIO_META_DNS_CAPTURE: "true"
enablePrometheusMerge: true
#discoverySelector: # new in v1.10, choose which namespaces Istiod should watch for configurations of services,endpoints,deployments
#- matchLabels:
# istio-discovery: enabled # <- example label
# #env: prod
# #region: us-east-1
#- matchExpressions:
# - key: app
# operator: In
# values:
# - cassandrs
# - spark
EOF
) --dry-run
- Verify if there any clients are connected to Istio v1.10.0
kubectl create deployment sleep --image=curlimages/curl -- /bin/sleep 3650d
kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- curl istiod-1-10-0.istio-system:15014/debug/connections | jq .
{
"totalClients": 0,
"clients": null
}
# Show all discovered endpoints
kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- curl istiod-1-10-0.istio-system:15014/debug/endpointz | jq . # ~1800+ lines for empty Minikube
- Sidecar proxy automatic injection by telling a namespace which revision (aka control plane) to select/use.
kubectl label namespace default istio.io/rev=1-10-0 istio-injection-
Note: The istio-injection label must be removed because it takes precedence over the istio.io/rev label for backward compatibility.
- Upgrade with Canary tag revision for isolated testing
# Tag the new control-plane version with 'canary' tag
istioctl experimental revision tag set canary --revision 1-10-0
Revision tag "canary" created, referencing control plane revision "1-10-0". To enable injection using this
revision tag, use 'kubectl label namespace <NAMESPACE> istio.io/rev=canary'
# Show tagged revision
istioctl experimental revision list
REVISION TAG ISTIO-OPERATOR-CR PROFILE REQD-COMPONENTS
1-10-0 canary istio-system/installed-state-control-plane-1-10-0 minimal base
istiod
# Update a namespace label to use the newly tagged control-plane for the injected sidecars to use it/connect to it
kubectl label namespace default istio.io/rev=canary --overwrite
# Restart deployments for new proxy to be injected, test the application and if all is good delete the "app canary deployment" and continue with full rollout of all deployments.
- Install ingress-gateway
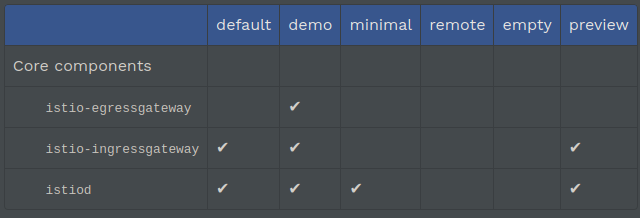
We install the ingress-gateway components separated in a separated namespace istio-ingrss. This is to allow to upgrade CP and IGW components independent. We achieve this using 'minimal' profile that includes only control CP components. Then for IGW install we use 'empty' profile that adds only the ingress-gateway. More about included components in each of profiles
# Create ingress own namespace
kubectl create ns istio-ingress
# Install revision
REVISION='--revision 1-10-0'
istioctl install -y -n istio-ingress $REVISION -f <(cat <<EOF
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
name: istio-ingressgateway
spec:
profile: empty # uses the 'empty' profile and enables the istio-ingressgateway component
hub: gcr.io/istio-release
components:
ingressGateways:
- name: istio-ingressgateway
namespace: istio-ingress # if not set defaults to 'istio-system'
enabled: true
k8s:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 2
service:
type: LoadBalancer
overlays:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: istio-ingressgateway
patches:
- path: spec.template.spec.containers[name:istio-proxy].lifecycle
value:
preStop:
exec:
command: ["sh", "-c", "sleep 5"]
EOF
) --dry-run
# Verify
# | Note that 'revision' relates to control-plane thus ingressgateway 'installed-state-istio-ingressgateway-1-10-0' installation
# | does hot have revision set
## Show IstioOperator installations
kubectl -n istio-system get istiooperators.install.istio.io
NAME REVISION STATUS AGE
installed-state-control-plane-1-10-0 1-10-0 165m
installed-state-istio-ingressgateway-1-10-0 1-10-0 8m47s
## Show revisions
istioctl experimental revision list
REVISION TAG ISTIO-OPERATOR-CR PROFILE REQD-COMPONENTS
1-10-0 canary istio-system/installed-state-control-plane-1-10-0 minimal base
istiod
istio-system/installed-state-istio-ingressgateway-1-10-0 empty ingress:istio-ingressgateway
## Test
GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}")
# With Gateway and VirtualService we can route traffic to a destination service via IngressGateway
curl -H "Host: example.com" http://$GATEWAY_IP
Note: As the next step IngressGateway can be integrated with Cert Manager
- Reduce Gateway Config
# Show what services IngressGateway has discovered, the list has even those that no routing is defined istioctl pc clusters deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system # Set PILOT_FILTER_GATEWAY_CLUSTER_CONFIG environment variable in the istiod deployment # kind: IstioOperator # spec: # components: # pilot: # k8s: # env: # - name: PILOT_FILTER_GATEWAY_CLUSTER_CONFIG # value: "true"
- (Optional) Access logging for gateway only using EnvoyFilter
- Istio docs explain to enable Envoy's Access Logs for the entire service mesh
kubectl apply -f <(cat <<EOF
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: ingressgateway-access-logging
namespace: istio-system
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
istio: ingressgateway
configPatches:
- applyTo: NETWORK_FILTER
match:
context: GATEWAY
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: "envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager"
patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
typed_config:
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager"
access_log:
- name: envoy.access_loggers.file
typed_config:
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.access_loggers.file.v3.FileAccessLog"
path: /dev/stdout
format: "[%START_TIME%] \"%REQ(:METHOD)% %REQ(X-ENVOY-ORIGINAL-PATH?:PATH)% %PROTOCOL%\" %RESPONSE_CODE% %RESPONSE_FLAGS% \"%UPSTREAM_TRANSPORT_FAILURE_REASON%\" %BYTES_RECEIVED% %BYTES_SENT% %DURATION% %RESP(X-ENVOY-UPSTREAM-SERVICE-TIME)% \"%REQ(X-FORWARDED-FOR)%\" \"%REQ(USER-AGENT)%\" \"%REQ(X-REQUEST-ID)%\" \"%REQ(:AUTHORITY)%\" \"%UPSTREAM_HOST%\" %UPSTREAM_CLUSTER% %UPSTREAM_LOCAL_ADDRESS% %DOWNSTREAM_LOCAL_ADDRESS% %DOWNSTREAM_REMOTE_ADDRESS% %REQUESTED_SERVER_NAME% %ROUTE_NAME%\n"
EOF
) --dry-run=server
- Check status
kubectl get -n istio-system istiooperators.install.istio.io NAME REVISION STATUS AGE installed-state-control-plane 3m57s installed-state-control-plane-1-9-1 1-9-1 2m34s installed-state-istio-ingressgateway-1-9-1 1-9-1 111s
- Uninstall
# This command uninstalls all revisions in default namespace of 'istio-system' istioctl x uninstall --purge # uninstall all istioctl x uninstall -f <(cat <<EOF ... EOF )
Install book info application
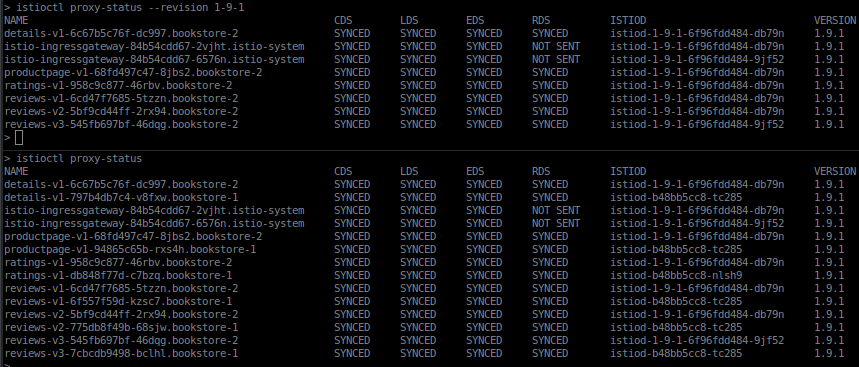
# Namespaces kubectl create ns bookstore-1 kubectl create ns bookstore-2 kubectl label namespace bookstore-1 istio-injection=enabled kubectl label namespace bookstore-2 istio.io/rev=1-9-1 istio-injection- kubectl get ns --show-labels NAME STATUS AGE LABELS bookstore-1 Active 155m istio-injection=enabled bookstore-2 Active 155m istio.io/rev=1-9-1 # Deploy application kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -n bookstore-1 kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -n bookstore-2 istioctl proxy-status --revision 1-9-1 # show only proxies of revision '1-9-1' istioctl proxy-status # show all proxies
You can see proxies connected only to revision '1-9-1' and at the bottom all proxies
Get info
Profiles are istiooperators.install.istio.io CRD manifests located in istio-1.7.3/manifests/profiles
# List profiles istioctl profile list ls istio-1.7.3/manifests/profiles default.yaml demo.yaml empty.yaml minimal.yaml preview.yaml remote.yaml # profile configuration istioctl profile dump demo istioctl profile dump --config-path components.pilot demo # Differences in the profiles istioctl profile diff default demo
Available dashboards commands
istioctl dashboard <dashboard> Available Commands: controlz Open ControlZ web UI envoy Open Envoy admin web UI grafana Open Grafana web UI jaeger Open Jaeger web UI kiali Open Kiali web UI prometheus Open Prometheus web UI zipkin Open Zipkin web UI
List all Istio CRDs
k get crd -A | grep istio | cut -f1 -d" " adapters.config.istio.io attributemanifests.config.istio.io authorizationpolicies.security.istio.io destinationrules.networking.istio.io envoyfilters.networking.istio.io gateways.networking.istio.io handlers.config.istio.io httpapispecbindings.config.istio.io httpapispecs.config.istio.io instances.config.istio.io istiooperators.install.istio.io peerauthentications.security.istio.io quotaspecbindings.config.istio.io quotaspecs.config.istio.io requestauthentications.security.istio.io rules.config.istio.io serviceentries.networking.istio.io sidecars.networking.istio.io templates.config.istio.io virtualservices.networking.istio.io workloadentries.networking.istio.io
IstioOperator
Output logs of istio-operator Kubernetes/Istio-logs-default-install when installing default istio+kiali=prometheus.
Initialize istio.operator
Note: This is being unfolded, check out here the second paragraph.
istioctl operator init # dump, remove, --force Using operator Deployment image: docker.io/istio/operator:1.7.3 ✔ Istio operator installed ✔ Installation complete # The operator deployment gets installed in a new namespace 'istio-operator' kubectl get deployment -n istio-operator -owide NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR istio-operator 1/1 1 1 7m14s istio-operator docker.io/istio/operator:1.7.3 name=istio-operator kubectl get all -n istio-operator NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/istio-operator-9dc6b7fd7-xf2m5 1/1 Running 0 5m42s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/istio-operator ClusterIP 10.119.252.73 <none> 8383/TCP 5m43s NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/istio-operator 1/1 1 1 5m43s NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/istio-operator-9dc6b7fd7 1 1 1 5m42s
Istio operator (v1.7.3), this is not super clear to me
find . -iname *operator* ./samples/operator ./samples/addons/extras/prometheus-operator.yaml ./manifests/charts/istio-operator # it's a chart to deploy operator ./manifests/charts/istio-operator/crds/crd-operator.yaml ./manifests/charts/base/crds/crd-operator.yaml ./manifests/charts/istio-telemetry/prometheusOperator ./manifests/deploy/crds/istio_v1alpha1_istiooperator_crd.yaml ./manifests/deploy/crds/istio_v1alpha1_istiooperator_cr.yaml ./manifests/deploy/operator.yaml # this [1] ./manifests/examples/customresource/istio_v1alpha1_istiooperator_cr.yaml
- [1]
manifests/deploy/operator.yaml
<syntaxhighlightjs lang=yaml> --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata:
namespace: istio-operator name: istio-operator
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: istio-operator
... </syntaxhighlightjs>
This API get always installed
k -n istio-system get istiooperators.install.istio.io # kind: IstioOperator
CRDs aka new kind: objects - demystified
- Istio terminology
- Use workload over service that can be misinterpreted by some
- Envoy terminiology Host, Downstream, Upstream, Listener, Cluster, Mesh, Runtime configuration
- Cluster: A cluster is a group of logically similar upstream hosts that Envoy connects to, eg. group of pods
reviewsservice v1, v2 and v3. - Cluster Discovery Service (CDS)
- Listener discovery service (LDS)
- Endpoint discovery service (EDS); cluster members are called endpoint.
- Route Discovery Service (RDS)
- Cluster: A cluster is a group of logically similar upstream hosts that Envoy connects to, eg. group of pods
VirtualServicesandDestinationRulesare key resources for configuring Istio’s traffic routing functionality.VirtualServices- is used to configure how requests are routed to a service within an Istio service mesh, define how traffic is routed to a given destinationDestinationRulesdefine policies that apply to traffic intended for a service after routing has occurred. ADestinationRulesis applied afterVirtualServicesrouting rules are evaluated, so they apply to the traffic’s real destination.subsets- defines a set of pods with common matching label eg.version: v1
gateways,gw- taps on to ingressgateway; describe which controller to use eg. plugs into real network received byservice/istio-ingressgatewaythat has labelistio=ingressgatewayvirtualservices,vs- it bounds to a gateway(s), and describes how requests are routed to a service within the meshdestinationrules,dr- applied aftervsrouting rules to real traffic destination, defines available versions called subsets, they name (using subsets) different revisions available and contain a logic (selector) of what corresponds to each revision.serviceentries,se- holds a list of all endpoints services that they belong to, adds an entry into Istio’s internal service registry, then the Envoy proxies can send traffic to the specified host as if it was a service in the mesh. Allows traffic to be managed for services running outside of the mesh,can set redirect, forward, retry, timeout and fault injection policies fro external destinations. Two purposes:- used as external service
- allows multi-cluster services
adaptersattributemanifestsauthorizationpolicies- defines policies of what service can access what workloadsenvoyfiltershandlershttpapispecbindingshttpapispecsinstancesistiooperatorspeerauthentications- defines what authenticated traffic within the cluster is allowed to access what workloads; used for service-to-service authentication to verify the client making the connectionquotaspecbindingsquotaspecsrequestauthentications- it's for humans outside of the cluster to validate their identity and decide to allow enter the clusterrulessidecarstemplatesworkloadentries
Customize istio installation
Configure ingress-gateways
- Deploying multiple Istio Ingress Gateways
- Creating an Internal Load Balancer in AWS EKS using Istio
- how-to-set-aws-alb-instead-of-elb-in-istio
- Istio: external AWS Application LoadBalancer and Istio Ingress Gateway published on 2021-04-22
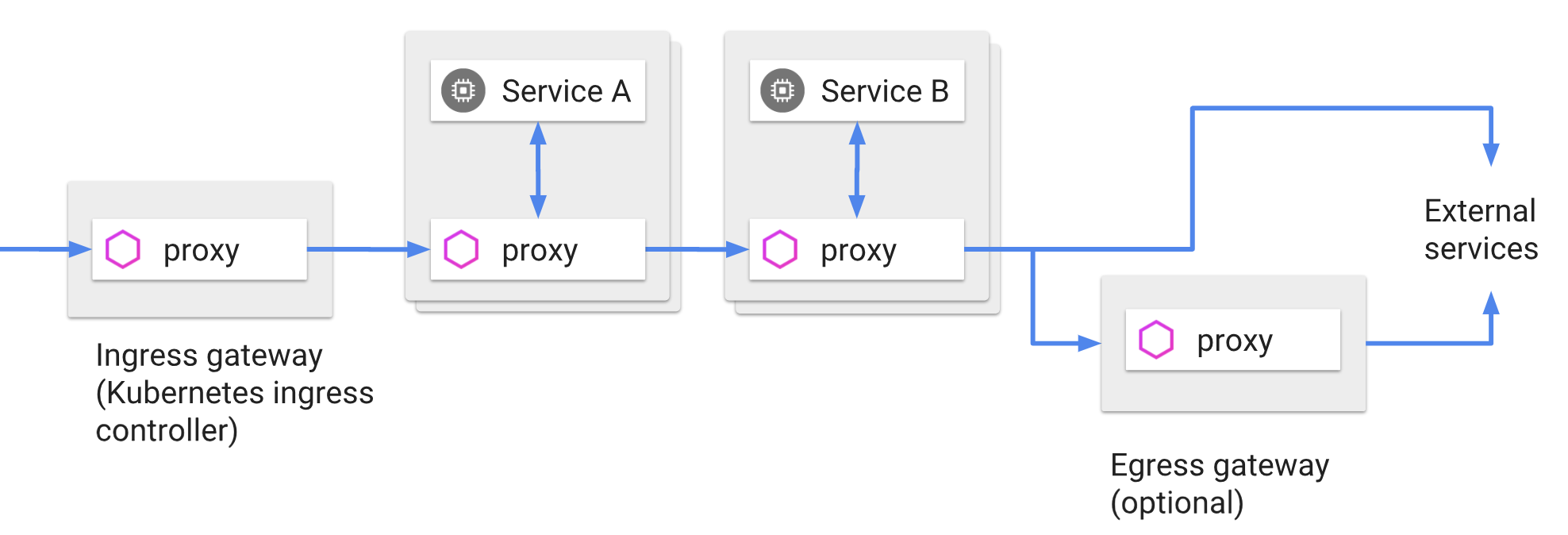
Gateways are a special type of component, since multiple ingress and egress gateways can be defined. In the IstioOperator API, gateways are defined as a list type. The default profile installs one ingress gateway, called istio-ingressgateway.
- Ingress Gateway
- describes a load balancer operating at the edge of the mesh that receives incoming HTTP/TCP connections.
- Egress Gateway
- An egress gateway configures a dedicated exit node for the traffic leaving the mesh, limiting which services can or should access external networks, or to enable secure control of egress traffic to add security to the mesh.
Show default values of the ingressgateway
istioctl profile dump --config-path components.ingressGateways istioctl profile dump --config-path values.gateways.istio-ingressgateway
Install istio with ingressgateway servioce as internal AWS loadbalancer:
istioctl install \ --set profile=default \ --set components.ingressGateways[0].enabled="true" \ --set components.ingressGateways[0].k8s.serviceAnnotations."service\.beta\.kubernetes\.io/aws-load-balancer-internal"=\"true\" ✔ Istio core installed ✔ Istiod installed ✔ Ingress gateways installed ✔ Installation complete # --set gateways.istio-ingressgateway.serviceAnnotations."service\.beta\.kubernetes\.io/aws-load-balancer-internal"="0\.0\.0\.0/0"
Configure using IstioOperator
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
profile: default
components:
ingressGateways:
- enabled: true # default is true for default profile
name: istio-ingressgateway # required key
egressGateways:
- enabled: true
name: istio-egressgateway # required key
EOF
) --dry-run
Ingress Gateways - controller - get details
# manually inject the sidecar
kubectl -n bin apply -f <(istioctl kube-inject -f httpbin.yaml)
export INGRESS_HOST=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
# AWS, uses 'hostname'
export INGRESS_HOST=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}')
export INGRESS_PORT=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].port}')
export SECURE_INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="https")].port}')
# Optional
export TCP_INGRESS_PORT=$( kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="tcp")].port}')
# Verify
env | grep INGRESS
Ingressgateway Kubernetes service
The istio istio-ingressgateway works as any other ingress controller, it has service type: LoadBalancer, that creates an endpoint with 4 ports, these in turn make external-loadbalancer to listen on these ports:
Port Name Protocol 8443 https TCP 15443 tls TCP 15021 status-port TCP 8080 http2 TCP
so, any incoming traffic via the ext-lb will end up being processed by istio-egressgateway-54884d6c57-mqgbg pod according to it's configuration that in reality is Envoy config built by pilot using using Istio CRDs.
Describe the service and the endpoint
vagrant@vagrant:~$ k -n istio-system describe svc istio-ingressgateway
Name: istio-ingressgateway
Namespace: istio-system
Labels: app=istio-ingressgateway
...
Selector: app=istio-ingressgateway,istio=ingressgateway
Type: LoadBalancer
IP: 10.119.253.21
LoadBalancer Ingress: 34.76.42.198
Port: status-port 15021/TCP
TargetPort: 15021/TCP
NodePort: status-port 32231/TCP
Endpoints: 10.116.19.12:15021
Port: http2 80/TCP
TargetPort: 8080/TCP
NodePort: http2 31604/TCP
Endpoints: 10.116.19.12:8080
Port: https 443/TCP
TargetPort: 8443/TCP
NodePort: https 30747/TCP
Endpoints: 10.116.19.12:8443
Port: tls 15443/TCP
TargetPort: 15443/TCP
NodePort: tls 31901/TCP
Endpoints: 10.116.19.12:15443
vagrant@vagrant:~$ k -n istio-system describe ep istio-ingressgateway
Name: istio-ingressgateway
Namespace: istio-system
Labels: app=istio-ingressgateway
...
Annotations: <none>
Subsets:
Addresses: 10.116.19.12 # -> target: istio-ingressgateway-86f88b6f6-7mzf7
NotReadyAddresses: <none>
Ports:
Name Port Protocol
---- ---- --------
https 8443 TCP
tls 15443 TCP
status-port 15021 TCP
http2 8080 TCP
General traffic flow
Note: This overview applies to each workload including Ingress-gateways
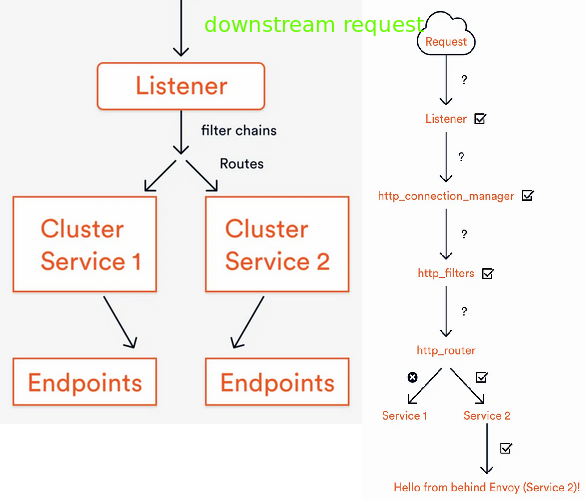
The arrows in the diagram show the flow of a request through the configuration, and the five key elements are the ‘listener,’ ‘filter chains,’ ‘routes,’ ‘clusters,’ and ‘endpoints’. The route is part of the filter chain, which is part of the listener.
- listener - 'binds' to a port and listens for inbound requests. Any request that comes in via another port would not be seen or handled by Envoy. In Envoy terms, it manages downstream requests
- filter chain - after being accepted by 'the listener', describes how the request should be handled once it’s entered Envoy
- route - extension of the filter chain, takes the HTTP request information and directs it to the correct service
- cluster - address IP:port that are the backend for a service. A cluster is a group of logically similar upstream hosts that Envoy connects to. Envoy discovers the members of a cluster via CDS(Cluster Discovery Service).
- endpoints - network nodes that implement a logical service. They are grouped into clusters. Endpoints in a cluster are upstream of an Envoy proxy.
Ingress-gateway - routes verification
INGRESS_GATEWAY_LABEL=ingressgateway # ingressgateway-internal|external
INGRESS_GATEWAY_POD=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio=$INGRESS_GATEWAY_LABEL -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
# Get listeners, other options: bootstrap,cluster,endpoint,listener,log,route,secret
istioctl proxy-config listeners -n istio-system $INGRESS_GATEWAY_POD
ADDRESS PORT MATCH DESTINATION
0.0.0.0 8080 ALL Route: http.80
0.0.0.0 15021 ALL Inline Route: /healthz/ready*
0.0.0.0 15090 ALL Inline Route: /stats/prometheus*
# Show routes, and virtual-services
istioctl proxy-config routes -n istio-system $INGRESS_GATEWAY_POD
NOTE: This output only contains routes loaded via RDS.
NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
http.80 alertmanager.staging.net /* alertmanager.monitoring
http.80 grafana.staging.net /* grafana.monitoring
http.80 prometheus.staging.net /* prometheus.monitoring
* /healthz/ready*
* /stats/prometheus*
Object examples
Gateway, virtualservice
# istio-1.7.3/samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
---
# Entry point gateway
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway # use istio default controller
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
# Routes traffic to destination, could use subset for Traffic Shifting
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: bookinfo
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- bookinfo-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /productpage
- uri:
prefix: /static
- uri:
exact: /login
- uri:
exact: /logout
- uri:
prefix: /api/v1/products
route:
- destination:
host: productpage
port:
number: 9080
#subset: v1 # [1] if defined in DestinationRule for the host ('productpage'), it will route to any pods
# matching a label(s) defined in the subset
# samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: productpage
spec:
host: productpage
subsets: # pod selectors matching labels
- name: v1 # [1] subset name for the host 'productpage'
labels:
version: v1
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: reviews
spec:
host: reviews
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
- name: v3
labels:
version: v3
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: ratings
spec:
host: ratings
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
- name: v2-mysql
labels:
version: v2-mysql
- name: v2-mysql-vm
labels:
version: v2-mysql-vm
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: details
spec:
host: details
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
---
# Split traffic between reviews:v1 and reviews:v3
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: reviews
spec:
hosts:
- reviews
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: reviews
subset: v1
weight: 50
- destination:
host: reviews
subset: v3
weight: 50
ServiceEntry
It intercepts any traffic from pods in the mesh (pods having envoy proxy installed) that matches the spec.hosts then applies meshConfig.outboundTrafficPolicy policy ALLOW_ANY or REGISTRY_ONLY plus additional features like retry, timeout etc. if configured.
It depends on installation option meshConfig.outboundTrafficPolicy.mode that configures Envoy's handling of unknown services, that is, services that are not defined in Istio’s internal service registry:
- ALLOW_ANY by default, so may not be defined in the configMap/istio, tells Envoy to let calls to unknown services pass through, this also means that Istio's capabilities cannot be applied to these endpoints
- REGISTRY_ONLY tells Envoy to block any connections to endpoints without a registry entry
kubectl get configmap istio -n istio-system -o yaml | grep mode -m1 -B1
Set REGISTRY_ONLY policy
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
profile: default
values:
meshConfig:
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
outboundTrafficPolicy:
mode: REGISTRY_ONLY
EOF
)
Example MESH_EXTERNAL service entry adds the ext-svc external dependency to Istio’s service registry. Required when REGISTRY_ONLY policy is set.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: google
spec:
hosts:
- www.google.com # FQDN of external resource or wildcard prefix
ports:
- number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
location: MESH_EXTERNAL # treat the service as external part of the mesh
resolution: DNS # | MESH_INTERNAL - Treat remote cluster services as part of the service mesh
# | as all clusters in the service mesh share the same root of trust.
peerauthentications and requestauthentications
peerauthentications- defines what authenticated traffic within the cluster is allowed to access what workloads; used for service-to-service authentication to verify the client making the connection. mutualTLS is used for transport authentication, Authentication policies apply to requests that a service receives.
apiVersion: "security.istio.io/v1beta1"
kind: "PeerAuthentication"
metadata:
name: "example-peer-policy"
namespace: "foo"
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: reviews
mtls:
mode: STRICT # PERMISSIVE, DISABLE
requestauthentications- it's for humans outside of the cluster to validate their identity and decide to allow enter the cluster, used for end-user authentication to verify credentials attached to the request.
apiVersion: "security.istio.io/v1beta1"
kind: "RequestAuthentication"
metadata:
name: "jwt-example"
namespace: istio-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
istio: ingressgateway # requires end-user JWT for ingress gateway
jwtRules:
- issuer: "testing@secure.istio.io"
jwksUri: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.5/..
# ^ it's authentication token not authorization is being evaluated in this policy
authorizationpolicies
These can be compare to Kubernetes NetworkPolicies but much more powerful as being aware of L7 and not only packet level traffic.
authorizationpolicies- defines policies of what service can access what workloads; authorisation features provides mesh-level, namespace-level, and workload-level access control on workloads in an Istio Mesh.
There is no need to explicitly enable Istio’s authorisation feature, only the AuthorizationPolicy needs applying on workloads to enforce access control.
If no AuthorizationPolicy applies to a workload, no access control will be enforced, In other words, all requests will be allowed. If any AuthorizationPolicy applies to a workload, access to that workload is denied by default, unless explicitly allowed by a rule declared in the policy.
# allow-all policy full access to all workloads in the default namespace
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-all
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- {}
---
# deny-all policy to all workloads in admin namespace
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: deny-all
namespace: admin
spec:
{}
Policies can distinguish in between authenticated and not authenticated users/services by specifying rules. There are reach configuration options so you may want to see docs.
code
spec:
rules:
- from:
- source:
principals: ["cluster.local/ns/default/sa/sleep"]
- source:
namespaces: ["dev"]
</syntaxhighlight>
Addons and integrations
Note: In v1.7.x the installation of telemetry addons by istioctl is deprecated, these are being managed now using addons integrations.
Kiali visualisations
Note: Example needs redoing. Istio v1.6.8 requires kiali secret, v1.7.x by default no authentication is enabled
! values.kiali.enabled is deprecated; use the samples/addons/ deployments instead ! values.prometheus.enabled is deprecated; use the samples/addons/ deployments instead ! addonComponents.kiali.enabled is deprecated; use the samples/addons/ deployments instead ! addonComponents.prometheus.enabled is deprecated; use the samples/addons/ deployments instead
You install kiali manually from scratch or pass arg to istioctl
# Create user name and password
KIALI_USERNAME=admin
KIALI_PASSPHRASE=admin
kubectl apply -f <(cat <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kiali
namespace: istio-system
labels:
app: kiali
stringData:
username: $KIALI_USERNAME
passphrase: $KIALI_PASSPHRASE
EOF
)
- Install - Option 1
cd istio-1.#.#/samples/addons kubectl apply -f kiali.yaml
- Deprecated installation options
Option 2 - istioctl - deprecated in v1.8
istioctl manifest install \ --set values.kiali.enabled=true \ --set values.prometheus.enabled=true
Option 3 - IstioOperator manifest, this is desired configuration defaults are set is not specified, then installed what is set, any resources not default and not specified will be pruned. Deprecated in v1.8.
| Basic | No auth |
|---|---|
| <syntaxhighlightjs lang=bash>
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: profile: default
values:
kiali:
enabled: true
prometheus:
enabled: true
EOF ) </syntaxhighlightjs> |
<syntaxhighlightjs lang=bash>
istioctl manifest install -f <(cat <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: profile: default
meshConfig:
# For debugging
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
addonComponents:
# Kiali uses Prometheus to populate its dashboards
prometheus:
enabled: true
kiali:
enabled: true
namespace: kiali
k8s:
podAnnotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "true"
values:
kiali:
prometheusAddr: http://prometheus.istio-system:9090
dashboard:
auth:
strategy: anonymous
EOF ) </syntaxhighlightjs> |
Verify installation and access the console
kubectl wait --for=condition=Available deployment/kiali -n istio-system --timeout=300s # Access the dashboard istioctl dashboard kiali
Add custom headers
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: httpbin
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- httpbin-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /headers
route:
- destination:
port:
number: 8000
host: httpbin
headers:
response: # add to response
add:
"key1": "abc"
request: # add to request
add:
"key2": "def"
Handling Istio Sidecars in Kubernetes Jobs
A Job/CronJob is not considered complete until all containers have stopped running, and Istio Sidecars run indefinitely.
Option 1: Disabling Istio Sidecar injection
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: 'false'
Option 2: Use `pkill` to stop the Istio Process
Add pkill -f /usr/local/bin/pilot-agent inside Dockerfile command and shareProcessNamespace: true to the Pod spec (not the Job spec).
Istio 1.3 and Core k8s Support (unverified)
<job shell script aka command:> curl -X POST http://127.0.0.0/quitquitquit
Debugging
Analize
istioctl analyze --all-namespaces istioctl analyze samples/bookinfo/networking/*.yaml istioctl analyze --use-kube=false samples/bookinfo/networking/*.yaml # Enable live analyzer, it will add to the status field eg.<code>status.validationMessages.type.code: IST0101</code> istioctl install --set values.global.istiod.enableAnalysis=true
Debug a singular pod or a deployment pods
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: redis
labels:
istio.io/rev: asm-173-6
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: debug-pod
namespace: redis
labels:
app: debug-pod
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: debug-pod
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: debug-pod
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/logLevel: debug # <- enable debug mode
spec:
containers:
- image: samos123/docker-toolbox
name: debug-pod
Istiocli debug commands
istioctl experimental describe pod <pod-name>[.<namespace>] istioctl proxy-status # | SYNCED means that Envoy has acknowledged the last configuration Istiod has sent to it. # | NOT SENT means that Istiod hasn’t sent anything to Envoy. This usually is because Istiod has nothing to send. # | STALE means that Istiod has sent an update to Envoy but has not received an acknowledgement. This usually indicates a networking issue between Envoy and Istiod or a bug with Istio itself. # Retrieve information about cluster configuration for the Envoy instance in a specific pod: istioctl proxy-config cluster <pod-name> [flags] # To retrieve information about bootstrap configuration for the Envoy instance in a specific pod: istioctl proxy-config bootstrap <pod-name> [flags] # To retrieve information about listener configuration for the Envoy instance in a specific pod: istioctl proxy-config listener <pod-name> [flags] # To retrieve information about route configuration for the Envoy instance in a specific pod: istioctl proxy-config route <pod-name> [flags] # To retrieve information about endpoint configuration for the Envoy instance in a specific pod: istioctl proxy-config endpoints <pod-name> [flags] istioctl proxy-config endpoints productpage-v1-6c886ff494-7vxhs --cluster "outbound|9080||reviews.default.svc.cluster.local"
Istio helm starter
Project by Salesforce to scaffold a helm chart with Istio that uses helm-starter plugin.
# Install `helm-starter` helm plugin helm plugin install https://github.com/salesforce/helm-starter.git # Fetch starter templates: mesh-service, ingress-service, mesh-egress, auth-policy helm starter fetch https://github.com/salesforce/helm-starter-istio.git # Create a helm chart from the starter helm create NAME --starter helm-starter-istio/[starter-name] for starter in mesh-service ingress-service mesh-egress auth-policy; do helm create authservice-$starter --starter helm-starter-istio/$starter; done
Important labels
Deployment <syntaxhighlightjs lang="yaml"> apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: Template:.Values.service # <- Istio label
version: Template:.Values.version # <- Istio label
template:
metadata:
labels:
# Kubernetes recommended labels
app.kubernetes.io/name: Template:.Values.service
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: Template:.Values.system
app.kubernetes.io/version: Template:.Values.version
# Isio required labels
app: Template:.Values.service # <- Istio label
version: Template:.Values.version # <- Istio label
Template:- if .Values.configMap
annotations:
checksum/config: Template:Include (print $.Template.BasePath "/configmap.yaml") .
spec:
containers:
Template:- range .Values.ports
- name: Template:.name containerPort: Template:.targetPort protocol: TCP # <-- TCP|HTTP or any other that is accepted
Template:- end </syntaxhighlightjs>
Service
<syntaxhighlightjs lang="yaml">
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
spec:
ports:
Template:- range .Values.ports
- name: Template:.name # <- tcp-<name>, http-<name>, grcp-<name> port: Template:.port targetPort: Template:.targetPort protocol: TCP # <- TCP|HTTP or any other that is accepted
Template:- end </syntaxhighlightjs>
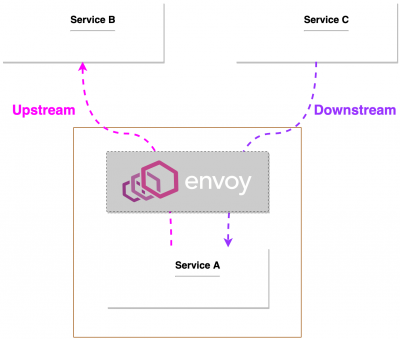
Envoy
- Upstream connections are the service Envoy is initiating the connection to.
- Downstream connections are the client that is initiating a request through Envoy.
Terminology in my own words:
- Listeners
- Declaration of ports to open on the proxy and listen for incoming connections
- Clusters
- Backend service to which we can route traffic. Also a group of logically similar upstream hosts that Envoy connects to
- Envoy Discovery (XDS)
Envoy is driven by a set of APIs that configure certain aspects of the proxy. We saw earlier how we specified clusters, listeners, and routes. We can also configure those over Envoy's xDS APIs:
- Listener discovery service (LDS)
- Route discovery service (RDS)
- Cluster discovery service (CDS)
- Service discovery service (SDS/EDS)
- Aggregated discovery service (ADS)
Now we don't have to specify listeners ahead of time. We can open them up or close them at runtime. Below example of Envoy config for dynamic Listeners configuration, set/received from api_config_source.
<syntaxhighlightjs lang="yaml">
dynamic_resources:
lds_config:
api_config_source:
api_type: GRPC
grpc_services:
- envoy_grpc:
cluster_name: xds_cluster
</syntaxhighlightjs> Configuring Envoy through this API is exactly what Istio's control plane does. With Istio we specify configurations in a more user-friendly format and Istio translates that configuration into something Envoy can understand and delivers this configuration through Envoy's xDS API.
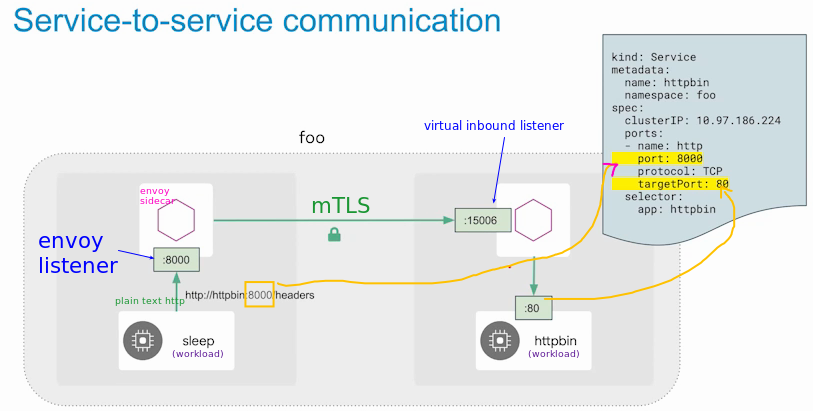
Service-to-service communication
This is zoom in on inbound connection from the sleep to http pod.
.
Troubleshooting
# Interrogate envoy stats endpoint kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- curl http://envoy:15000/stats| grep retry
Troubleshooting istio
Check istiod endpoint, get registry
# Get all services in the Istio registry, workloads are also included even if they are not officially part of the mesh kubectl exec -n istio-system -it deploy/istiod-1-8-4 -- pilot-discovery request GET /debug/registryz kubectl exec -n istio-system -it deploy/istiod-1-8-4 -- pilot-discovery version # [discovery,help,request,version]
Verify an app/pod iptables modified by istio-proxy. This rules are in the Network kernel namespace hold by the pod.
# List iptables rules - this should fail
kubectl -n default exec -it deploy/httpbin -c istio-proxy -- sudo iptables -L -t nat
sudo: effective uid is not 0, is /usr/bin/sudo on a file system with the 'nosuid' option set or an NFS file system without root privileges?
# Grant the proxy sidecar privileges escalation
kubectl edit deploy/httpbin -n default
containers:
- name: istio-proxy
image: docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.8.4
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: true # by default it's false
privileged: true # by default it's false
# Show iptables - 15006(incoming) and 15001(outgoing) traffic interception
kubectl -n default exec -it deploy/httpbin -c istio-proxy -- sudo iptables -L -t nat | grep -e ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT -e 15006 -e ISTIO_REDIRECT -e 15001
ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere
Chain ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT (3 references)
REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere redir ports 15006
ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT all -- anywhere !localhost owner UID match istio-proxy
ISTIO_IN_REDIRECT all -- anywhere !localhost owner GID match istio-proxy
ISTIO_REDIRECT all -- anywhere anywhere
Chain ISTIO_REDIRECT (1 references)
REDIRECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere redir ports 15001
We can see here iptables is used to redirect incoming and outgoing traffic to Istio's data plane proxy. Incoming traffic goes to port 15006 of the Istio proxy while outgoing traffic will go through 15001. If we check the Envoy listeners for those ports, we can see exactly how the traffic gets handled.
- IngressGateway
Query the gateway configuration to get all routes
istioctl proxy-config routes deploy/istio-ingressgateway.istio-system
NOTE: This output only contains routes loaded via RDS.
NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
http.80 example.com /* web-api-gw-vs.default
* /stats/prometheus*
* /healthz/ready*
# Show details of a single route
istioctl proxy-config routes deploy/istio-ingressgateway.istio-system --name http.80 -o json
Resources
- gitops-istio Istio on a Kubernetes cluster and automating A/B testing and canary releases with GitOps pipelines example
Training Istio v1.5
- What is Istio Service Mesh?
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 1
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 2 - Enabling Sidecar Injection
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 3 - Visualizing the System with Kiali
- Istio Hands on Demo Part 4 - Finding Performance Problems
- istio-fleetman Github source materials
- Istio Architecture Part 1 - Proxies
- Istio Architecture Part 2 - The Data Plane and Envoy
- Istio Architecture Part 3 - The Control Plane
- Istio Architecture Part 4 - Going Deeper into Envoy
- istio-cheatsheet by Tetratate A+++
Istio v1.7
- VM <-> K8s mesh demo at 30 min
Semi-related
Related technology
- Introduction to HTTP/2 http/2 is used by Envoy internally