Difference between revisions of "Azure/General"
< Azure
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
*[https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli-windows?view=azure-cli-latest Install Azure CLI on Windows] | *[https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli-windows?view=azure-cli-latest Install Azure CLI on Windows] | ||
== Powershell AZModule == | |||
<source> | <source> | ||
PS C:> Get-InstalledModule -Name Az -AllVersions | select Name,Version | PS C:> Get-InstalledModule -Name Az -AllVersions | select Name,Version | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 30 April 2019
Generalising Windows machine before creating an image
- Create Windows VM
- Provision/baseline your VM by RDPing and installing software
- Generalise your system using sysprep to create System Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE)
- Win+R, type sysprep, it will take you to C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep and run sysprep.exe
- System Cleanup Action: Enter System Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE)
- Generalize: Yes (tick)
- Shutdown Options: Reboot
- Optional run:
C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep\sysprep.exe /oobe /generalize /shutdown /mode:vm - You will be disconnected from RDP but the instance still run generalising and will stop once done
- Win+R, type sysprep, it will take you to C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep and run sysprep.exe
- Go to Azure portal and click on Capture to create an image now
- You find new image in Images service where you can create new VM from
Generalising Linux machine before creating an image
- Create Linux VM
- Provision/baseline your VM by SSHing to provisioning your software
- Generalise your system using Azure Linux Agent - waagent
sudo waagent -deprovision+user- account you are currently logged in will be completly deleted including home
- Linux system does not neet to be shut
- Go to Azure portal and click on Capture to create an image now
- You find new image in Images service where you can create new VM from
Not supported server roles and services
This section has been updated on 26/09/2018, for upto date information see 1.
The following roles are not supported on Microsoft Azure virtual machines:
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server
- Hyper-V (Hyper-V role is supported in Azure Ev3, and Dv3 series VMs only)
- Rights Management Services
- Windows Deployment Services
- Windows Server features
The following significant features are not supported:
- BitLocker Drive Encryption (on the operating system hard disk, may be used on data disks)
- Internet Storage Name Server
- Multipath I/O
- Network Load Balancing
- Peer Name Resolution Protocol
- RRAS
- DirectAccess
- SNMP Services
- Storage Manager for SANs
- Windows Internet Name Service
- Wireless LAN Service
Terminology
- Azure subscription
- Used to pay for Azure cloud services. You can have many subscriptions and they're linked to a credit card.
- Azure tenant
- A dedicated and trusted instance of Azure AD that's automatically created when your organization signs up for a Microsoft cloud service subscription, such as Microsoft Azure, Microsoft Intune, or Office 365. An Azure tenant represents a single organization.
- Single tenant
- Azure tenants that access other services in a dedicated environment are considered single tenant.
- Multi-tenant
- Azure tenants that access other services in a shared environment, across multiple organizations, are considered multi-tenant.
- Azure AD directory
- Each Azure tenant has a dedicated and trusted Azure AD directory. The Azure AD directory includes the tenant's users, groups, and apps and is used to perform identity and access management functions for tenant resources.
- Azure AD account
- An identity created through Azure AD or another Microsoft cloud service, such as Office 365. Identities are stored in Azure AD and accessible to your organization's cloud service subscriptions. This account is also sometimes called a Work or school account.
- Owner
- This role helps you manage all Azure resources, including access. This role is built on a newer authorization system called role-base access control (RBAC) that provides fine-grained access management to Azure resources. For more information, see Classic subscription administrator roles, Azure RBAC roles, and Azure AD administrator roles.
- Azure AD Global administrator
- This administrator role is automatically assigned to whomever created the Azure AD tenant. Global administrators can perform all of the administrative functions for Azure AD and any services that federate to Azure AD, such as Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, and Skype for Business Online. You can have multiple Global administrators, but only Global administrators can assign administrator roles (including assigning other Global administrators) to users. Note: This administrator role is called Global administrator in the Azure portal, but it's called Company administrator in Microsoft Graph API, Azure AD Graph API, and Azure AD PowerShell.
- Microsoft account (also called, MSA)
- Personal accounts that provide access to your consumer-oriented Microsoft products and cloud services, such as Outlook, OneDrive, Xbox LIVE, or Office 365. Your Microsoft account is created and stored in the Microsoft consumer identity account system that's run by Microsoft.
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Manage your guest users and external partners, while maintaining control over your own corporate data.
- Business-to-Customer (B2C)
- Customize and control how users sign up, sign in, and manage their profiles when using your apps.
Resources
- Terminiology AD official
Azure tools
- az - Azure CLI
- Powershell AZModule to copy files - requires PS 5.1+
- blob storage .msi
- Powershell DSC Desired State Configuration system
- VMagent custom script extension - runs on Azure VMs, allows to run one-off scripts
az - Azure CLI
Download and install msi
PS C:> wget https://aka.ms/installazurecliwindows PS C:> wget https://azurecliprod.blob.core.windows.net/msi/azure-cli-2.0.63.msi
Login and basic commands
PS C:> az login PS C:> az account show --output table EnvironmentName IsDefault Name State TenantId ----------------- ----------- --------------------------- ------- ------------------------------------ AzureCloud True Microsoft Azure Sponsorship Enabled aaaaaaaa-bbbb-4a1a-9b26-bac3cb7dcccc
Resources
Powershell AZModule
PS C:> Get-InstalledModule -Name Az -AllVersions | select Name,Version PS C:> Install-Module -Name Az -AllowClobber# PS C:> Connect-AzAccount #connect
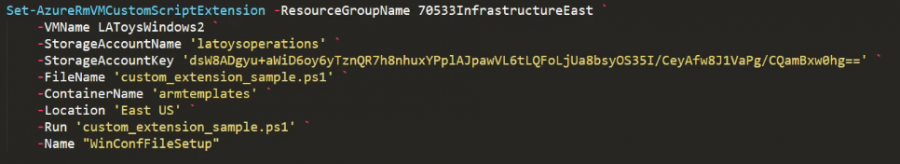
VMagent custom script extension
Windows
$fileUri = @("https://xxxxxxx.blob.core.windows.net/buildServer1/1_Add_Tools.ps1",
"https://xxxxxxx.blob.core.windows.net/buildServer1/2_Add_Features.ps1",
"https://xxxxxxx.blob.core.windows.net/buildServer1/3_CompleteInstall.ps1")
$Settings = @{"fileUris" = $fileUri};
$storageaccname = "xxxxxxx"
$storagekey = "1234ABCD"
$ProtectedSettings = @{"storageAccountName" = $storageaccname; "storageAccountKey" = $storagekey; "commandToExecute" = "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -File 1_Add_Tools.ps1"};
#run command
Set-AzureRmVMExtension -ResourceGroupName myRG `
-Location myLocation `
-VMName myVM `
-Name "buildserver1" `
-Publisher "Microsoft.Compute" `
-ExtensionType "CustomScriptExtension" `
-TypeHandlerVersion "1.9" `
-Settings $Settings `
-ProtectedSettings $ProtectedSettings
Linux
az vm extension set \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --vm-name myVM --name customScript \ --publisher Microsoft.Azure.Extensions \ --settings ./script-config.json
Resources
Resources
- What is and can't be suppoerted on Azure Windows systems
- Minimum version support for Linux and Windows virtual machine agents in Azure Linux systems
- Azure for AWS Administrators
- Blog resources
- Tips and tricks 100+