Difference between revisions of "Kubernetes/Security and RBAC"
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
<source lang=bash> | <source lang=bash> | ||
kubectl -n rbac1 exec -it apitest-<UID> -- /bin/sh #connect to the container shell | kubectl -n rbac1 exec -it apitest-<UID> -- /bin/sh #connect to the container shell | ||
root | |||
root | #display token and namespace that allows to connect to API server from this pod | ||
root$ cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/{token,namespace} | |||
#call API server to list K8s services in 'rbac' namespace | |||
root$ curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/rbac/services | |||
</source> | </source> | ||
Revision as of 22:49, 6 July 2019
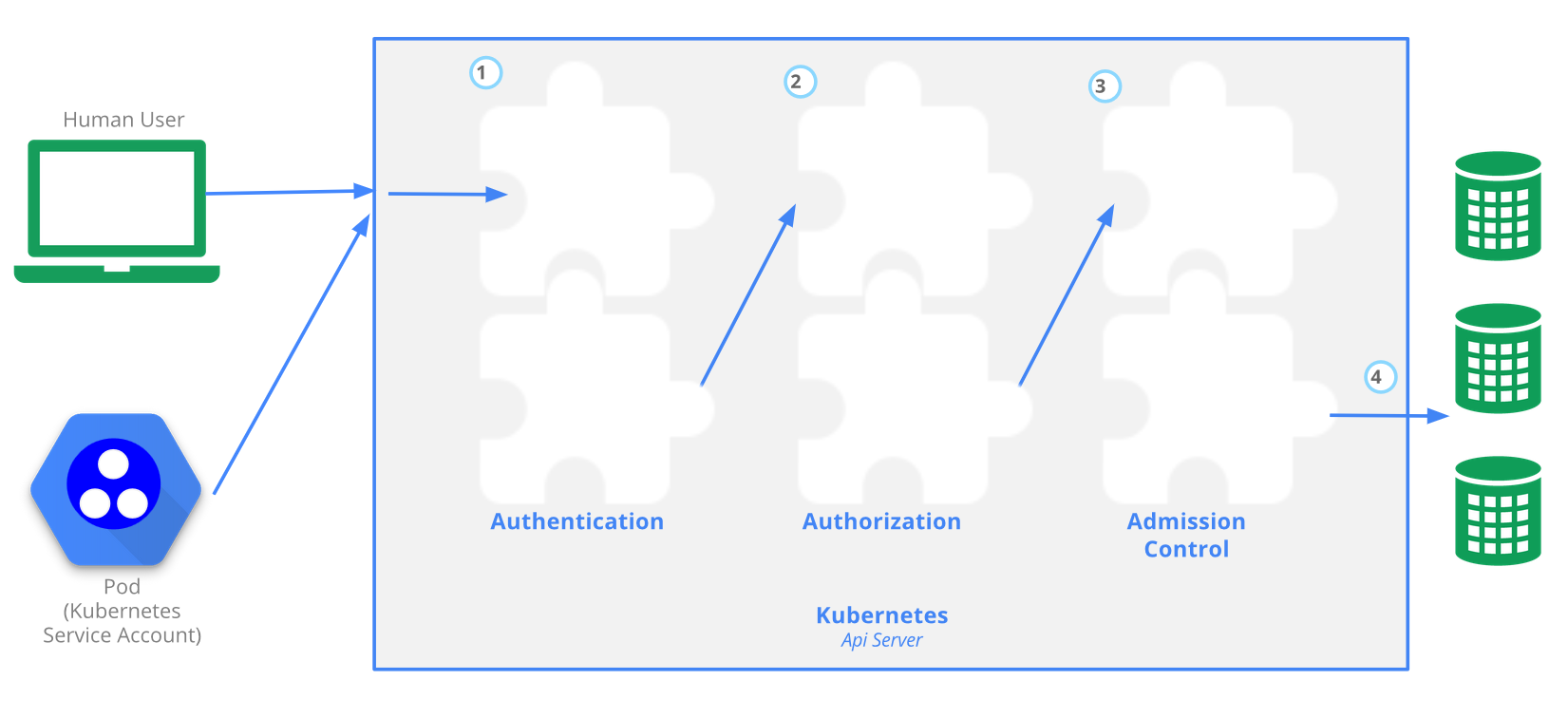
API Server and Role Base Access Control
The Kubernetes API server provides CRUD actions (Create, Read, Update, Delete) interface for interacting with cluster state over a RESTful API. API calls can come only from 2 sources:
- kubectl
- POD
There is 4 stage process
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Admission
- Writing configuration CRUD actions to etcd database
RBAC is managed by 4 resources, divided over 2 groups
| Group-1 namespace resources | Group-2 cluster level resources | resources type |
|---|---|---|
| roles | cluster roles | defines what can be done |
| role bindings | cluster role bindings | defines who can do it |
When deploying a pod a default serviceaccount is assigned if not specified in the pod manifest. The serviceaccount represents an identity of an app running on a pod. Token file holds authentication token. Let's create a namespace and create a test pod to try to list available services.
kubectl create ns rbac kubectl run apitest --image=nginx -n rbac #create test container, to run API call test from
Each pod has serviceaccount, the API authentication token is on a pod. When a pod makes API call uses the token, this allows to assumes the serviceaccount, so it gets identity. You can preview the token on the pod.
kubectl -n rbac1 exec -it apitest-<UID> -- /bin/sh #connect to the container shell
#display token and namespace that allows to connect to API server from this pod
root$ cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/{token,namespace}
#call API server to list K8s services in 'rbac' namespace
root$ curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/rbac/services
List all serviceaccounts. Serviceaccounts can only be used within the same namespace.
kubectl get serviceaccounts -n rbac kubectl get secrets NAME TYPE DATA AGE default-token-qqzc7 kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 39h kubectl get secrets default-token-qqzc7 -o yaml #display secrets