Difference between revisions of "HashiCorp/Vagrant"
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
end | end | ||
= Chef_solo = | == Chef_solo == | ||
Create recipe, the following dirctory structure is required, eg. recipe name is: vagrant_la | Create recipe, the following dirctory structure is required, eg. recipe name is: vagrant_la | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 1 August 2017
Install
Check your distro most likely Ubuntu version candidate
apt-cache vagrant
Download from https://releases.hashicorp.com/vagrant/1.9.5/vagrant_1.9.5_x86_64.deb
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/vagrant/1.9.5/vagrant_1.9.5_x86_64.debb sudo dpkg -i vagrant_1.9.5_x86_64.deb sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -f #to resolve missing dependencies if any
Install ruby is recommended as configuration within Vagrant file is written in Ruby language.
sudo apt-get install ruby sudo gem install bundler sudo gem update bundler #if update needed
Getting started
- Create Vagrant project, by creating Vagrantfile in your current directory
vagrant init #initializes an project vagrant init ubuntu/xenial64 # initializes project with Ubuntu16.04 Official Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) Daily Build
- Add boxes (standard VMs from providers in Virtualbox, VMware or Hyper-V format)
vagrant box add hashicorp/precise64 #username: hashicorp boximage: precise64, this is preconfigured repository
#Box can be specified via URLs or local file paths, Virtualbox can only nest 32bit machines
vagrant box add --force ubuntu/14.04 https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/vagrant/trusty/current/trusty-server-cloudimg-amd64-vagrant-disk1.box
vagrant box add --force ubuntu/14.04-i386 https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/vagrant/precise/current/precise-server-cloudimg-i386-vagrant-disk1.box
- Manage boxes using
vagrant box list | add | remove
- Configure Vagrantfile to use the box as your base system
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/14.04-i386" #or ubuntu/xenial64 for official Ubuntu16.04LTS
config.vm.hostname = "ubuntu" #hostname, requires reload
end
- Power up your Vagrant box
vagrant up
Error:
Timed out while waiting for the machine to boot. This means that
Vagrant was unable to communicate with the guest machine within
the configured ("config.vm.boot_timeout" value) time period.
...
The error above is due to Virtualbox cannot run nested 64bit virtualbox VM. Spinning up a 64bit VM stops with an error that no 64bit CPU could be found.
- Ssh to the box
piotr@vm-ubuntu64:~/git/vagrant$ vagrant ssh #default password is "vagrant" vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-precise-32:~$ w 13:08:35 up 15 min, 1 user, load average: 0.06, 0.31, 0.54 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT vagrant pts/0 10.0.2.2 13:02 1.00s 4.63s 0.09s w
- Shared directory between Vagrant VM and an hypervisor provider
Vagrant VM shares a directory mounted at /vagrant with the directory on the host containing your Vagrantfile
- Delete Vagrant VM
vagrant destroy
- Delete downloaded Vagrant VM image file
vagrant box remove
Sync folders
First folder is on a host machine and the second is mapped on Vagrant guest vm.
Disabling
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.sync_folder "../data/", "/vagrant-data", disabled: true
end
Modifying the Owner/Group
config.vm.sync_folder "../data/", "/vagrant-data", disabled: true, owner: "root", group: "root"
Networking - port forwarding
Vagrant can forward any host(hypervisor) TCP port to guest vm specyfing in ~/git/vargant/Vagrant file
config.vm.network :forwarded_port, guest: 80, host: 4567
Reload Vagrant VM
vagrant reload
Run on the host from a web browser http://127.0.0.1:4567 to test it.
Vagrant power states
vagrant suspend- saves the current running state of the machine and stop itvagrant halt- gracefully shuts down the guest operating system and power down the guest machinevagrant destroy- removes all traces of the guest machine from your system. It'll stop the guest machine, power it down, and remove all of the guest hard disks
Vagrant providers
Vagrant can work with a wide variety of backend providers, such as VMware, AWS, and more without changing Vagrantfile. It's enough to specify the provider and Vagrant will do the rest:
vagrant up --provider=vmware_fusion vagrant up --provider=aws
Build using a provisioning script (shell provisioner)
Vagrant can run from shared location script or from inline: Vagrant file shell provisioning commands.
Create provisioning script
vi ~/git/vagrant/bootstrap.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
export http_proxy=http://username:password@proxyserver.local:8080
export https_proxy=$http_proxy
apt-get update
apt-get install -y apache2
if ! [ -L /var/www ]; then
rm -rf /var/www
ln -fs /vagrant /var/www #configures that shared directory will be Apache DocumentRoot directory
fi
Configure Vagrant to run this shell script above when setting up our machine
vi ~/git/vagrant/Vagrantfile
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/14.04-i386"
#the provision line tells Vagrant to use the shell provisioner to setup the machine
config.vm.provision :shell, path: "bootstrap.sh"
end
Bring the environment up
vagrant up #runs provisioning only once vagrant reload --provision #reloads VM skipping import and runs provisioning vagrant ssh #ssh to VM wget -qO- 127.0.0.1 #test Apache is running on VM
- Provisioners - shell, ansible, ansible_local and more
This section is about using Ansible with Vagrant,
*ansible, where Ansible is executed on the Vagrant host *ansible_local, where Ansible is executed on the Vagrant guest
Specify Ansible as a provisioner in Vagrant file
# # Run Ansible from the Vagrant Host # config.vm.provision "ansible" do |ansible| ansible.playbook = "playbook.yml" end
Chef_solo
Create recipe, the following dirctory structure is required, eg. recipe name is: vagrant_la
├── cookbooks │ └── vagrant_la │ └── recipes │ └── default.rb Vagrant
vi cookbooks/vagrant_la/recipes/default.rb
execute "apt-get update"
package "apache2"
execute "rm -rf /var/www"
link "var/www" do
to "/vagrant"
end
In Vagrant file add following
config.vm.provision "chef_solo" do |chef|
chef.add_recipe "vagrant_la"
end
Run vagrant up
Vagrant box images
vagrant box list #list all downloaded boxes
Default path of boxes image
C:\Users\%username%\.vagrant.d\boxes #Windows ~/.vagrant.d/boxes #LInux
Change default path via environment variable
export VAGRANT_HOME=my/new/path/goes/here/
Enable Vagrant to use proxy server for VMs
Install proxyconf:
vagrant plugin install vagrant-proxyconf
Configure your Vagrantfile, here particularly host 10.0.0.1:3128 runs CNTLM proxy
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.proxy.http = "http://10.0.0.1:3128"
config.proxy.https = "http://10.0.0.1:3128"
config.proxy.no_proxy = "localhost,127.0.0.1"
Virtualbox Guest Additions - upgrade
Find out what version you run
$ lsmod | grep -io vboxguest | xargs modinfo | grep -iw version version: 4.3.36_Ubuntu
or
$ sudo /usr/sbin/VBoxService --version 4.3.36_Ubuntur105129
Download the extension, you can explore here
wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/5.0.32/VBoxGuestAdditions_5.0.32.iso
wip... see references for the rest of steps, next step instal vagrant plugin vb...
References
List all Virtualbox SSH redirections
vboxmanage list vms | cut -d ' ' -f 2 > /tmp/vms.out && for vm in $(cat /tmp/vms.out); do vboxmanage showvminfo "$vm" | grep ssh; done vboxmanage list vms | cut -d ' ' -f 1 | sed 's/"//g' > /tmp/vms.out && for vm in $(cat /tmp/vms.out); do echo $vm; vboxmanage showvminfo "$vm" | grep ssh; done vboxmanage list vms | cut -d ' ' -f 1 | sed 's/"//g' > /tmp/vms.out && for vm in $(cat /tmp/vms.out); do vboxmanage showvminfo "$vm" | grep ssh | tr --delete '\n'; echo " $vm"; done
sed 's/"//g' #removes double quotes from whole string tr --delete '\n' #deletes EOL, so the next command output is appended to the previous line
Print connections count in line
while true; do echo -n `ss -at | wc -l`" " ; sleep 3; done
Example Vagrantfile by building a simple cluster
git clone https://github.com/jweissig/episode-45
This creates Ansible mgmt server, Load Balancer and Web nodes [1..2]. HAProxy will be configured via Ansible code.
# Defines our Vagrant environment
#
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# create mgmt node
config.vm.define :mgmt do |mgmt_config|
mgmt_config.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
mgmt_config.vm.hostname = "mgmt"
mgmt_config.vm.network :private_network, ip: "10.0.15.10"
mgmt_config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "256"
end
mgmt_config.vm.provision :shell, path: "bootstrap-mgmt.sh"
end
# create load balancer
config.vm.define :lb do |lb_config|
lb_config.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
lb_config.vm.hostname = "lb"
lb_config.vm.network :private_network, ip: "10.0.15.11"
lb_config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
lb_config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "256"
end
end
# create some web servers
# https://docs.vagrantup.com/v2/vagrantfile/tips.html
(1..2).each do |i|
config.vm.define "web#{i}" do |node|
node.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
node.vm.hostname = "web#{i}"
node.vm.network :private_network, ip: "10.0.15.2#{i}"
node.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: "808#{i}"
node.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "256"
end
end
end
end
Boot strap script bootstrap-mgmt.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash # install ansible (http://docs.ansible.com/intro_installation.html) apt-get -y install software-properties-common apt-add-repository -y ppa:ansible/ansible apt-get update apt-get -y install ansible # copy examples into /home/vagrant (from inside the mgmt node) cp -a /vagrant/examples/* /home/vagrant chown -R vagrant:vagrant /home/vagrant # configure hosts file for our internal network defined by Vagrantfile cat >> /etc/hosts <<EOL # vagrant environment nodes 10.0.15.10 mgmt 10.0.15.11 lb 10.0.15.21 web1 10.0.15.22 web2 10.0.15.23 web3 10.0.15.24 web4 10.0.15.25 web5 10.0.15.26 web6 10.0.15.27 web7 10.0.15.28 web8 10.0.15.29 web9 EOL
Gitbash path - /c/Program\ Files/Oracle/VirtualBox/VBoxManage.exe
Set bootstrap script for Proxy or No-proxy specific system
Vagrant status Vagrant up Vagrant ssh mgmt ansible all --list-hosts ssh-keyscan web1 web2 lb > ~/.ssh/known_hosts ansible-playbook ssh-addkey.yml -u vagrant --ask-pass ansible-playbook site.yml
Once set it up you can navigate on your laptop to:
http://localhost:8080/ #Website test http://localhost:8080/haproxy?stats #HAProxy stats
Use to verify end server
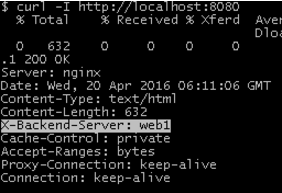
curl -I http://localhost:8080
Generate web traffic
vagrant ssh lb sudo apt-get install apache2-utils ansible localhost -m apt -a "pkg=apache2-utils state=present" --become ab -n 1000 -c 1 http://10.0.2.15:80/
The above is a curtsy of sysadmincasts.com can be git cloned:
git clone https://github.com/jweissig/episode-45
Resources
- Vagrant Start up documentation
- Vagrant Hashicorp VMs repository Virtualbox
- Vagrant Ubuntu VMs images Virtualbox
- Vagrant and Ansible provisioner Vagrant docs