Difference between revisions of "HashiCorp/Vagrant"
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
;Configure Vagrantfile to use the box as your base system | ;Configure Vagrantfile to use the box as your base system | ||
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| | Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| | ||
config.vm.box = "<span style="color: green">ubuntu/14.04-i386</span>" | config.vm.box = "<span style="color: green">ubuntu/14.04-i386</span>" #or ubuntu/xenial64 for official Ubuntu16.04LTS | ||
config.vm.hostname = "ubuntu" #hostname, requires reload | config.vm.hostname = "ubuntu" #hostname, requires reload | ||
end | end | ||
Revision as of 20:57, 19 June 2017
Install
Check your distro most likely Ubuntu version candidate
apt-cache vagrant
Download from https://releases.hashicorp.com/vagrant/1.9.5/vagrant_1.9.5_x86_64.deb
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/vagrant/1.9.5/vagrant_1.9.5_x86_64.debb sudo dpkg -i vagrant_1.9.5_x86_64.deb sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -f #to resolve missing dependencies if any
Install ruby is recommended as .vagrant file is using it
sudo apt-get install ruby sudo gem install bundler sudo gem update bundler #if update needed
Getting started
- Create Vagrant project, by creating Vagrantfile in your current directory
vagrant init #initializes an project vagrant init ubuntu/xenial64 # initializes project with Ubuntu16.04 Official Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (Xenial Xerus) Daily Build
- Add boxes (standard VMs from providers in Virtualbox, VMware or Hyper-V format)
vagrant box add hashicorp/precise64 #username: hashicorp boximage: precise64, this is preconfigured repository
#Box can be specified via URLs or local file paths, Virtualbox can only nest 32bit machines
vagrant box add --force ubuntu/14.04 https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/vagrant/trusty/current/trusty-server-cloudimg-amd64-vagrant-disk1.box
vagrant box add --force ubuntu/14.04-i386 https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/vagrant/precise/current/precise-server-cloudimg-i386-vagrant-disk1.box
- Configure Vagrantfile to use the box as your base system
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/14.04-i386" #or ubuntu/xenial64 for official Ubuntu16.04LTS
config.vm.hostname = "ubuntu" #hostname, requires reload
end
- Power up your Vagrant box
vagrant up
Error:
Timed out while waiting for the machine to boot. This means that
Vagrant was unable to communicate with the guest machine within
the configured ("config.vm.boot_timeout" value) time period.
...
The error above is due to Virtualbox cannot run nested 64bit virtualbox VM. Spinning up a 64bit VM stops with an error that no 64bit CPU could be found.
- Ssh to the box
piotr@vm-ubuntu64:~/git/vagrant$ vagrant ssh #default password is "vagrant" vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-precise-32:~$ w 13:08:35 up 15 min, 1 user, load average: 0.06, 0.31, 0.54 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT vagrant pts/0 10.0.2.2 13:02 1.00s 4.63s 0.09s w
- Shared directory between Vagrant VM and an hypervisor provider
Vagrant VM shares a directory mounted at /vagrant with the directory on the host containing your Vagrantfile
- Delete Vagrant VM
vagrant destroy
- Delete downloaded Vagrant VM image file
vagrant box remove
Build using a provisioning script (shell provisioner)
Vagrant can run from shared location script or from inline: Vagrant file shell provisioning commands.
Create provisioning script
vi ~/git/vagrant/bootstrap.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
export http_proxy=http://username:password@proxyserver.local:8080
export https_proxy=$http_proxy
apt-get update
apt-get install -y apache2
if ! [ -L /var/www ]; then
rm -rf /var/www
ln -fs /vagrant /var/www #configures that shared directory will be Apache DocumentRoot directory
fi
Configure Vagrant to run this shell script above when setting up our machine
vi ~/git/vagrant/Vagrantfile
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/14.04-i386"
#the provision line tells Vagrant to use the shell provisioner to setup the machine
config.vm.provision :shell, path: "bootstrap.sh"
end
Bring the environment up
vagrant up #runs provisioning only once vagrant reload --provision #reloads VM skipping import and runs provisioning vagrant ssh #ssh to VM wget -qO- 127.0.0.1 #test Apache is running on VM
- Provisioners - shell, ansible, ansible_local and more
This section is about using Ansible with Vagrant,
*ansible, where Ansible is executed on the Vagrant host *ansible_local, where Ansible is executed on the Vagrant guest
Specify Ansible as a provisioner in Vagrant file
# # Run Ansible from the Vagrant Host # config.vm.provision "ansible" do |ansible| ansible.playbook = "playbook.yml" end
- Networking - port forwarding
Vagrant can forward any host(hypervisor) TCP port to guest vm specyfing in ~/git/vargant/Vagrant file
config.vm.network :forwarded_port, guest: 80, host: 4567
Reload Vagrant VM
vagrant reload
Run on the host from a web browser http://127.0.0.1:4567 to test it.
- Vagrant power states
vagrant suspend- saves the current running state of the machine and stop itvagrant halt- gracefully shuts down the guest operating system and power down the guest machinevagrant destroy- removes all traces of the guest machine from your system. It'll stop the guest machine, power it down, and remove all of the guest hard disks
- Vagrant providers
Vagrant can work with a wide variety of backend providers, such as VMware, AWS, and more without changing Vagrantfile. It's enough to specify the provider and Vagrant will do the rest:
vagrant up --provider=vmware_fusion vagrant up --provider=aws
Vagrant box images
vagrant box list #list all downloaded boxes
Default path of boxes image
C:\Users\%username%\.vagrant.d\boxes #Windows ~/.vagrant.d/boxes #LInux
Change default path via environment variable
export VAGRANT_HOME=my/new/path/goes/here/
Enable Vagrant to use proxy server for VMs
Install proxyconf:
vagrant plugin install vagrant-proxyconf
Configure your Vagrantfile, here particularly host 10.0.0.1:3128 runs CNTLM proxy
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.proxy.http = "http://10.0.0.1:3128"
config.proxy.https = "http://10.0.0.1:3128"
config.proxy.no_proxy = "localhost,127.0.0.1"
Virtualbox Guest Additions - upgrade
Find out what version you run
$ lsmod | grep -io vboxguest | xargs modinfo | grep -iw version version: 4.3.36_Ubuntu
or
$ sudo /usr/sbin/VBoxService --version 4.3.36_Ubuntur105129
Download the extension, you can explore here
wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/5.0.32/VBoxGuestAdditions_5.0.32.iso
wip... see references for the rest of steps, next step instal vagrant plugin vb...
References
List all Virtualbox SSH redirections
vboxmanage list vms | cut -d ' ' -f 2 > /tmp/vms.out && for vm in $(cat /tmp/vms.out); do vboxmanage showvminfo "$vm" | grep ssh; done vboxmanage list vms | cut -d ' ' -f 1 | sed 's/"//g' > /tmp/vms.out && for vm in $(cat /tmp/vms.out); do echo $vm; vboxmanage showvminfo "$vm" | grep ssh; done vboxmanage list vms | cut -d ' ' -f 1 | sed 's/"//g' > /tmp/vms.out && for vm in $(cat /tmp/vms.out); do vboxmanage showvminfo "$vm" | grep ssh | tr --delete '\n'; echo " $vm"; done
sed 's/"//g' #removes double quotes from whole string tr --delete '\n' #deletes EOL, so the next command output is appended to the previous line
Example Vagrantfile by building a simple cluster
git clone https://github.com/jweissig/episode-45
This creates Ansible mgmt server, Load Balancer and Web nodes [1..2]. HAProxy will be configured via Ansible code.
# Defines our Vagrant environment
#
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# create mgmt node
config.vm.define :mgmt do |mgmt_config|
mgmt_config.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
mgmt_config.vm.hostname = "mgmt"
mgmt_config.vm.network :private_network, ip: "10.0.15.10"
mgmt_config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "256"
end
mgmt_config.vm.provision :shell, path: "bootstrap-mgmt.sh"
end
# create load balancer
config.vm.define :lb do |lb_config|
lb_config.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
lb_config.vm.hostname = "lb"
lb_config.vm.network :private_network, ip: "10.0.15.11"
lb_config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
lb_config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "256"
end
end
# create some web servers
# https://docs.vagrantup.com/v2/vagrantfile/tips.html
(1..2).each do |i|
config.vm.define "web#{i}" do |node|
node.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
node.vm.hostname = "web#{i}"
node.vm.network :private_network, ip: "10.0.15.2#{i}"
node.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: "808#{i}"
node.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "256"
end
end
end
end
Boot strap script bootstrap-mgmt.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash # install ansible (http://docs.ansible.com/intro_installation.html) apt-get -y install software-properties-common apt-add-repository -y ppa:ansible/ansible apt-get update apt-get -y install ansible # copy examples into /home/vagrant (from inside the mgmt node) cp -a /vagrant/examples/* /home/vagrant chown -R vagrant:vagrant /home/vagrant # configure hosts file for our internal network defined by Vagrantfile cat >> /etc/hosts <<EOL # vagrant environment nodes 10.0.15.10 mgmt 10.0.15.11 lb 10.0.15.21 web1 10.0.15.22 web2 10.0.15.23 web3 10.0.15.24 web4 10.0.15.25 web5 10.0.15.26 web6 10.0.15.27 web7 10.0.15.28 web8 10.0.15.29 web9 EOL
Gitbash path - /c/Program\ Files/Oracle/VirtualBox/VBoxManage.exe
Set bootstrap script for Proxy or No-proxy specific system
Vagrant status Vagrant up Vagrant ssh mgmt ansible all --list-hosts ssh-keyscan web1 web2 lb > ~/.ssh/known_hosts ansible-playbook ssh-addkey.yml -u vagrant --ask-pass ansible-playbook site.yml
Once set it up you can navigate on your laptop to:
http://localhost:8080/ #Website test http://localhost:8080/haproxy?stats #HAProxy stats
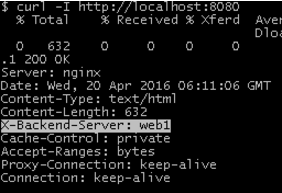
Use to verify end server
curl -I http://localhost:8080
Generate web traffic
vagrant ssh lb sudo apt-get install apache2-utils ansible localhost -m apt -a "pkg=apache2-utils state=present" --become ab -n 1000 -c 1 http://10.0.2.15:80/
The above is a curtsy of sysadmincasts.com can be git cloned:
git clone https://github.com/jweissig/episode-45
Resources
- Vagrant Start up documentation
- Vagrant Hashicorp VMs repository Virtualbox
- Vagrant Ubuntu VMs images Virtualbox
- Vagrant and Ansible provisioner Vagrant docs